Home > Press > Researchers Develop Integrated Dual-mode Active and Passive Infrared Camera: Based on type-II superlattices, high-performance infrared camera could aid search-and-rescue missions
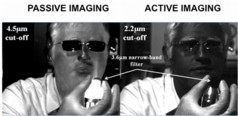 |
| A Center for Quantum Devices researcher holds a heater and a narrow-band filter centered at 3.6µm. The heater can be seen when imaged with the band-pass detectors sensitive up to 4.5µm (left), but not in the ones with shorter detection wavelengths up to 2.2µm (right). |
Abstract:
High-performance infrared cameras are crucial for civilian and military applications such as night-vision goggles and search-and-rescue operations. Existing cameras usually fall into one of two types: active cameras, which use an invisible infrared source to illuminate the scene, usually in the near or short-wavelength infrared; and passive cameras, which detect the thermal radiation given off by a warm object, typically in the mid- or long-wavelength infrared, without the need for any illumination. Both camera types have advantages and disadvantages in the field.
Researchers Develop Integrated Dual-mode Active and Passive Infrared Camera: Based on type-II superlattices, high-performance infrared camera could aid search-and-rescue missions
Chicago, IL | Posted on January 16th, 2013Integrating both modes of imaging into a single camera would open new possibilities — but doing so has proven challenging. Until now, dual-mode active and passive infrared cameras needed either two different infrared detectors or complex controllable filters to accommodate the different wavelengths, and then required additional signal processing to reconstruct a single image from the two modes.
However, in a move that may change the way we look a two-color imaging, researchers at the Northwestern University's Center for Quantum Devices have now found a way to integrate active and passive infrared imaging capability into a single chip. This opens the way to lighter and simpler dual-mode active/passive cameras with lower power dissipation.
A paper about the findings, "Active and Passive Infrared Imager Based on Short-Wave and Mid-Wave Type-II Superlattice Dual-Band Detectors," was published January 1 in the journal Optic Letters. The work was led by Manijeh Razeghi, Walter P. Murphy Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science in Northwestern's McCormick School of Engineering and Applied Science.
The researchers achieved this feat by engineering the quantum properties of novel semiconductor materials called the indium arsenide/gallium antimonide (InAs/GaSb) type-II superlattices. Researchers at the center have been pioneering the development of type-II superlattices as a superior replacement of aging mercury-cadmium-telluride (HgCdTe) infrared camera technology in terms of both performance and cost.
Using the unique band-structure engineering capabilities of type-II superlattices, they have developed a new structure incorporating two different superlattices with different layer spacings, thus enabling detection with a cutoff wavelength of either 2.2µm (active mode) or 4.5µm (passive mode). This new device can simply switch from passive to active mode by a very small change in bias.
The work was funded by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Megan Fellman
847-491-3115
Copyright © Northwestern University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








