Home > Press > Research by CU-Boulder physicists creates ‘recipe book’ for building new materials
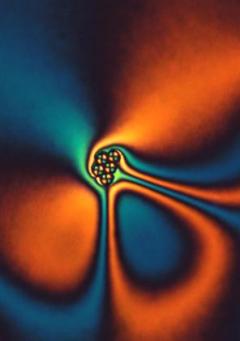 |
| This image shows polarized light interacting with a particle injected into a liquid crystal medium. Photo by CU-Boulder scientists Bohdan Senyuk and Ivan Smalyukh. |
Abstract:
By showing that tiny particles injected into a liquid crystal medium adhere to existing mathematical theorems, physicists at the University of Colorado Boulder have opened the door for the creation of a host of new materials with properties that do not exist in nature.
Research by CU-Boulder physicists creates ‘recipe book’ for building new materials
Boulder, CO | Posted on December 28th, 2012The findings show that researchers can create a "recipe book" to build new materials of sorts using topology, a major mathematical field that describes the properties that do not change when an object is stretched, bent or otherwise "continuously deformed." Published online Dec. 23 in the journal Nature, the study also is the first to experimentally show that some of the most important topological theorems hold up in the real material world, said CU-Boulder physics department Assistant Professor Ivan Smalyukh, a study senior author.
The research could lead to upgrades in liquid crystal displays, like those used in laptops and television screens, to allow them to interact with light in new and different ways. One possibility is to create liquid crystal displays that are even more energy efficient, Smalyukh said, extending the battery life for the devices they're attached to.
The research was funded in part by Smalyukh's Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers, which he received from President Barack Obama in 2010. And the research supports the goals laid out by the White House's Materials Genome Initiative, Smalyukh said, which seeks to deploy "new advanced materials at least twice as fast as possible today, at a fraction of the cost."
Smalyukh, postdoctoral researcher Bohdan Senyuk, and doctoral student Qingkun Liu set up the experiment by creating colloids — solutions in which tiny particles are dispersed, but not dissolved, throughout a host medium. Colloids are common in everyday life and include substances such as milk, jelly, paint, smoke, fog and shaving cream.
For this study, the physicists created a colloid by injecting tiny particles into a liquid crystal — a substance that behaves somewhat like a liquid and somewhat like a solid. The researchers injected differently shaped particles that represent fundamental building-block shapes in topology. That means each of the particles is distinct from the others and one cannot be turned into the other without cutting or gluing. Objects that look differently can still be considered the same in topology if one can be turned into the other by stretching or bending - types of "continuous deformations."
In the field of topology, for example, an object shaped like a donut and an object shaped like a coffee cup are treated the same. That's because a donut shape can be "continuously deformed" into a coffee cup by indenting one side of the donut. But a donut-shaped object cannot be turned into a sphere or a cylinder because the hole in the donut would have to be eliminated by "gluing" the sides of the donut back together or by "cutting" the side of the donut.
Once injected into a liquid crystal, the particles behaved as predicted by topology. "Our study shows that interaction between particles and molecular alignment in liquid crystals follows the predictions of topological theorems, making it possible to use these theorems in designing new composite materials with unique properties that cannot be encountered in nature or synthesized by chemists," Smalyukh said. "These findings lay the groundwork for new applications in experimental studies of low-dimensional topology, with important potential ramifications for many branches of science and technology."
The study was co-authored by Sailing He of Zhejiang University in China; Randall Kamien and Tom Lubensky of the University of Pennsylvania, and Robert Kusner of the University of Massachusetts, Amherst.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ivan Smalyukh
303-492-7277
Laura Snider
CU media relations
303-735-0528
Copyright © University of Colorado at Boulder
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








