Home > Press > New injectable gels toughen up after entering the body: These more durable gels could find applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering
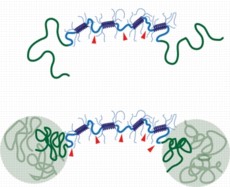 |
| When the new shear thinning hydrogel (top) is heated to body temperature, polymer chains join together to form a reinforcing network that improves the gel’s stability (bottom). Image: Matt Glassman |
Abstract:
Gels that can be injected into the body, carrying drugs or cells that regenerate damaged tissue, hold promise for treating many types of disease, including cancer. However, these injectable gels don't always maintain their solid structure once inside the body.
New injectable gels toughen up after entering the body: These more durable gels could find applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering
Cambridge, MA | Posted on November 19th, 2012MIT chemical engineers have now designed an injectable gel that responds to the body's high temperature by forming a reinforcing network that makes the gel much more durable, allowing it to function over a longer period of time.
The research team, led by Bradley Olsen, an assistant professor of chemical engineering, described the new gels in a recent issue of the journal Advanced Functional Materials. Lead author of the paper is Matthew Glassman, a graduate student in Olsen's lab. Jacqueline Chan, a former visiting student at MIT, is also an author.
Olsen and his students worked with a family of gels known as shear thinning hydrogels, which have a unique ability to switch between solid-like and liquid-like states. When exposed to mechanical stress — such as being pushed through an injection needle — these gels flow like fluid. But once inside the body, the gels return to their normal solid-like state.
However, a drawback of these materials is that after they are injected into the body, they are still vulnerable to mechanical stresses. If such stresses make them undergo the transition to a liquid-like state again, they can fall apart.
"Shear thinning is inherently not durable," Olsen says. "How do you undergo a transition from not durable, which is required to be injected, to very durable, which is required for a long, useful implant life?"
The MIT team answered that question by creating a reinforcing network within their gels that is activated only when the gel is heated to body temperature (37 degrees Celsius).
Shear thinning gels can be made with many different materials (including polymers such as polyethylene glycol, or PEG), but Olsen's lab is focusing on protein hydrogels, which are appealing because they can be designed relatively easily to promote biological functions such as cellular adhesion and cell migration.
The protein hydrogels in this study consist of loosely packed proteins held together by links between protein segments known as coiled coils, which form when two or three helical proteins coil into a ropelike structure.
The MIT researchers designed their hydrogel to include a second reinforcing network, which takes shape when polymers attached to the ends of each protein bind together. At lower temperatures, these polymers are soluble in water, so they float freely in the gel. However, when heated to body temperature, they become insoluble and separate out of the watery solution. This allows them to join together and form a sturdy grid within the gel, making it much more durable.
The researchers found that gels with this reinforcing network were much slower to degrade when exposed to mechanical stress and were significantly stiffer. This offers a promising way to thwart the tendency of shear thinning materials to erode once in the body, says Jason Burdick, an associate professor of bioengineering at the University of Pennsylvania.
"Building in this secondary network based on a different type of mechanism is a very elegant way to overcome that obstacle through material design," says Burdick, who was not part of the research team.
Another advantage of these gels is that they can be tuned to degrade over time, which would be useful for long-term drug release. The researchers are now working on ways to control this feature, as well as incorporating different types of biological functions into the gels.
The research was funded by the U.S. Army Research Office through MIT's Institute for Soldier Nanotechnologies (ISN). Potential applications of these nanostructured gels to soldier medicine include preventing blood loss, accelerating wound healing and protecting against infections and disease.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Caroline McCall
MIT News Office
E:
T: 617-253-1682
Copyright © MIT
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








