Home > Press > NIST study suggests carbon nanotubes may protect DNA from oxidation
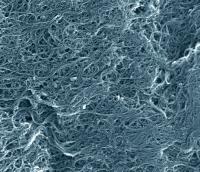 |
| Scanning electron microscope image of a typical sample of the NIST single-wall carbon nanotube soot standard reference material. Recent NIST research suggests that, at least in the laboratory, carbon nanotubes may help protect DNA molecules from damage by oxidation. The image shows an area just over a micrometer wide. (Color added for clarity.)
Credit: Credit: Vladar, NIST |
Abstract:
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have provided evidence in the laboratory that single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) may help protect DNA molecules from damage by oxidation. In nature, oxidation is a common chemical process in which a reactive chemical removes electrons from DNA and may increase the chance for mutations in cells. More studies are needed to see if the in vitro protective effect of nanotubes reported in the laboratory also occurs in vivo, that is, within a living organism.
NIST study suggests carbon nanotubes may protect DNA from oxidation
Gaithersburg, MD | Posted on November 15th, 2012"Our findings don't tell us whether carbon nanotubes are good or bad for people and the environment," says Elijah Petersen, one of the authors of the study. "However, the results do help us better understand the mechanisms by which nanotubes might interact with biomolecules."
Single-wall carbon nanotubes—tiny hollow rods that are one-atom-thick sheets of graphene rolled into cylinders 10,000 times smaller in diameter than a human hair—are prized for their extraordinary optical, mechanical, thermal and electronic properties. They are being used to produce lightweight and extremely strong materials, enhance the capabilities of devices such as sensors, and provide a novel means of delivering drugs with great specificity. However, as carbon nanotubes become increasingly incorporated into consumer and medical products, the public concern about their potential environmental, health and safety (EHS) risks has grown. Scientifically determining the level of risk associated with the carbon nanotubes has been challenging, with different studies showing conflicting results on cellular toxicity. One of the components lacking in these studies is an understanding of what physically happens at the molecular level.
In a recent paper,* NIST researchers investigated the impact of ultrasonication on a solution of DNA fragments known as oligomers in the presence and absence of carbon nanotubes. Ultrasonication is a standard laboratory technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to mix solutions, break open cells or process slurries. The process can break water molecules into highly reactive agents such as hydroxyl radicals and hydrogen peroxide that are similar to the oxidative chemicals that commonly threaten mammalian cell DNA, although the experimental levels from sonication are much greater than those found naturally within cells. "In our experiment, we were looking to see if the nanotubes enhanced or deterred oxidative damage to DNA," Petersen says.
Contrary to the expectation that carbon nanotubes will damage biomolecules they contact, the researchers found that overall levels of accumulated DNA damage were significantly reduced in the solutions with nanotubes present. "This suggests that the nanotubes may provide a protective effect against oxidative damage to DNA," Petersen says.
A possible explanation for the surprising result, Petersen says, is that the carbon nanotubes may act as scavengers, binding up the oxidative species in solution and preventing them from interacting with DNA. "We also saw a decrease in DNA damage when we did ultrasonication in the presence of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), a chemical compound known to be a hydroxyl radical scavenger," Petersen says.
Petersen says that a third experiment where ultrasonication was performed in the presence of DMSO and SWCNTs at the same time produced an additive effect, reducing the DNA damage levels more significantly than either treatment alone.
This research is part of NIST's work to help characterize the potential EHS risks of nanomaterials, and develop methods for identifying and measuring them.
* E.J. Petersen, X. Tu, M. Dizdaroglu, M. Zheng and B.C. Nelson. Protective roles of single-wall carbon nanotubes in ultrasonication-induced DNA base damage. Small (2012), DOI: 10/1002/smll.201201217.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Michael E. Newman
301-975-3025
Copyright © National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








