Home > Press > NIST research highlights promise of AFM-IR for quantitative nanoscale chemical analysis
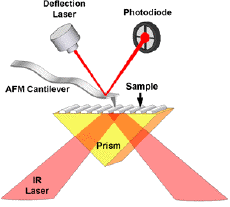 |
| Schematic to show the operation of AFM-IR |
Abstract:
Anasys Instruments announces a new paper authored by Dr Andrea Centrone and his colleagues at NIST published recently in Small*, a leading publication which focuses on the nano and micro worlds.
NIST research highlights promise of AFM-IR for quantitative nanoscale chemical analysis
Santa Barbara, CA | Posted on October 30th, 2012Dr Centrone's team reported on experiments that carefully studied the AFM-IR signal strength versus sample thickness. The experiments showed that the AFM-IR signal increases linearly with thickness for samples up to 1µm thick. This observed linearity may pave the way for quantitative chemical analysis at the nanoscale.
AFM-IR has recently attracted great interest in that it enables chemical identification and imaging with nanoscale resolution. In this paper, NIST reports on electron beam nanopatterned polymer samples which were fabricated directly on zinc selenide prisms and used to experimentally evaluate the AFM-IR signal lateral resolution, sensitivity and linearity. The authors have shown that the AFM-IR lateral resolution for chemical imaging is comparable to the lateral resolution obtained in the AFM topography. Spectra and chemical maps were produced from samples as thin as 40 nm. The observations also provide experimental confirmation of theoretical predictions on AFM-IR previously developed by Prof Alexandre Dazzi of Univ of Paris-Orsay who is also the inventor of the technique.
The patented AFM-IR technique is available commercially as the nanoIR™ platform from Anasys Instruments, Santa Barbara, CA. In AFM-IR, a rapidly pulsed infrared (IR) laser is directed on upon a thin sample which absorbs the IR light and undergoes rapid thermomechanical expansion. An AFM tip in contact with the sample resonates in response to the expansion, and this resonance is measured by the AFM. "We are excited by this through work by Dr. Centrone and his colleagues," said Craig Prater, Chief Technology Officer of Anasys Instruments. "We applaud NIST's research and involvement in advancing nanoscale characterization of materials using AFM-based spectroscopy."
For information about the AFM-IR products from Anasys Instruments, please visit www.anasysinstruments.com.
*Chemical imaging beyond the diffraction limit: experimental validation of the PTIR technique, DOI: 10.1001/smll.201200788. For a high resolution image of either of the above, please right click to download and save or contact Jezz Leckenby at Talking Science.
####
About Anasys Instruments
Anasys Instruments is dedicated to delivering innovative products and solutions that analyze samples with spatially varying physical and chemical properties at the micro and nanoscale. Anasys Instruments introduced the nanoTA in 2006 which pioneered the field of nanoscale thermal property measurement. In 2010, Anasys Instruments proudly introduced the award-winning breakthrough nanoIR™ Platform which pioneered the field of nanoscale IR measurement.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Anasys contact:
Roshan Shetty
Anasys Instruments Corporation
121 Gray Avenue, Suite 100
Santa Barbara
CA 93101 USA
Tel: +1 (805) 730-3310
Media contact:
Jezz Leckenby
Talking Science Limited
39 de Bohun Court
Saffron Walden
Essex CB10 2BA, UK
Tel +44 (0) 1799 521881
Mob +44 (0) 7843 012997
www.talking-science.com
Copyright © Anasys Instruments
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








