Home > Press > Nano-hillocks: Of mountains and craters
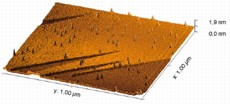 |
| Following bombardment with highly charged ions, nano-hillocks have formed in an area of localized melting. Atomic force microscope image. Picture: HZDR |
Abstract:
n the field of nanotechnology, electrically-charged particles are frequently used as tools for surface modification. Researchers at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) and the TU Vienna were at last able to reconcile important issues concerning the effects of highly charged ions on surfaces.
Nano-hillocks: Of mountains and craters
Dresden, Germany | Posted on October 1st, 2012Ion beams have been used for some time now for surface modification as ions are capable of carrying such high energies that a single particle alone can induce drastic changes to the surface under bombardment. Following careful examination, an international team of researchers was at last able to shed light on the reasons why sometimes craters and other times hillocks are forming as a result of this process. Their findings have recently been published in the scientific journal, Physical Review Letters.
Charge instead of speed
"If the goal is to deposit a maximum amount of energy on a tiny spot on the surface, it is of comparatively little use to simply bombard the surface with fast atoms," explains Prof. Friedrich Aumayr of the TU Vienna's Institute of Applied Physics. "Fast particles penetrate deep into the material thereby depositing their energy over a wide range." If, however, you first strip a large number of electrons from individual atoms and then allow these highly charged ions to collide with the material surface, the effects you get are quite dramatic as the energy that was previously required to ionize the atoms is now being released within a very small area of a few nanometers in diameter, and within an ultrashort time.
This can lead to melting of a very small volume of the material, loss of its orderly atomic structure, and, finally, its expansion. The large number of electronic excitations that result from the ion's interactions with the surface has a strong impact on the material and ultimately leads to the atoms being bumped out of position. The end-result is nano-hillock formation - the appearance of tiny protrusions on the material's surface. If the energy required to initiate melting of the material is insufficient, small holes or defects will form on or below the surface instead.
Elaborate experiments at the HZDR facility for highly charged ions were just as important to obtaining a detailed picture of the processes that take place at the material's surface as were computer simulations and extensive theoretical work. "At our new HZDR facility, we have the capabilities for deliberately forming nano-hillocks and nano-craters on surfaces. In close collaboration with the groups of our colleagues Friedrich Aumayr and Joachim Burgdörfer at the TU Vienna we succeeded to grasp the underlying physical mechanisms in more detail", explains Dr. Stefan Facsko. Egyptian physicist Dr. Ayman El-Said, who spent two years as a Humboldt Foundation fellow conducting research at HZDR, made substantial contributions to the current body of research in this field.
Assumptions confirmed
The scientists are calling their results the missing important piece of the puzzle to help them understand the interaction of highly charged ions with surfaces. By subjecting the sample to an acid treatment following ion bombardment, they are able to document the extent to which a surface is modified at given energies. The formation of nano-hillocks depends to a large extent on the ion beams' charge state and to a lesser extent on their velocity. The formation of craters, on the other hand, is dependent upon both the charge state and the kinetic energy of the ions. The Vienna and Dresden researchers had long suspected this and were now at last able to produce the necessary evidence obtained from their experiments conducted at the HZDR.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. René Heller
Institute of Ion Beam Physics and Materials Research at HZDR
Phone: +49 351 260-3617
Dr. Christine Bohnet
Press Officer
49-351-260-2450
oder +49 160 969 288 56
Copyright © Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








