Home > Press > All systems go at the biofactory
 |
Abstract:
In order to assemble novel biomolecular machines, individual protein molecules must be installed at their site of operation with nanometer precision. LMU researchers have now found a way to do just that. Green light on protein assembly!
All systems go at the biofactory
Munich, Germany | Posted on September 28th, 2012The finely honed tip of the atomic force microscope (AFM) allows one to pick up single biomolecules and deposit them elsewhere with nanometer accuracy. The technique is referred to as Single-Molecule Cut & Paste (SMC&P), and was developed by the research group led by LMU physicist Professor Hermann Gaub. In its initial form, it was only applicable to DNA molecules. However, the molecular machines responsible for many of the biochemical processes in cells consist of proteins, and the controlled assembly of such devices is one of the major goals of nanotechnology. A practical method for doing so would not only provide novel insights into the workings of living cells, but would also furnish a way to develop, construct and utilize designer nanomachines.
In a major step towards this goal, the LMU team has modified the method to allow them to take proteins from a storage site and place them at defined locations within a construction area with nanometer precision. "In liquid medium at room temperature, the "weather conditions" at the nanoscale are comparable to those in a hurricane," says Mathias Strackharn, first author of the new study. Hence, the molecules being manipulated must be firmly attached to the tip of the AFM and held securely in place in the construction area.
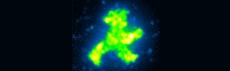
Traffic signals prove the efficiency
The forces that tether the proteins during transport and assembly must also be weak enough not to cause damage, and must be tightly controlled. To achieve these two goals, the researchers used a combination of antibodies, DNA-binding "zinc-finger" proteins, and DNA anchors. "We demonstrated the method's feasibility by bringing hundreds of fluorescent GFP molecules together to form a little green man, like the traffic-light figure that signals to pedestrians to cross the road, but only some micrometers high," Strackharn explains.
With this technique, functional aspects of complex protein machines - such as how combinations of different enzymes interact, and how close together they must be to perform coupled reactions - can be tested directly. A further goal is to develop artificial multimolecular assemblies modeled on natural "cellulosomes", which could be used to convert plant biomass into biofuels. Strackharn points out the implications: "If we can efficiently build mimics of these ‘enzymatic assembly lines' by bringing individual proteins together, we could perhaps make a significant contribution to the exploitation of sustainable energy sources." (JACS September 2012) göd
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Kathrin Bilgeri
49-892-180-6938
Copyright © Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








