Home > Press > Newly demonstrated capabilities of low-powered nanotweezers may benefit cellular-level studies
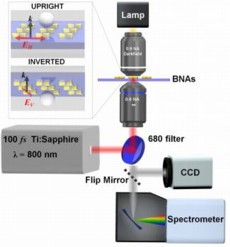 |
| Experimental setup schematic showing laser source, microscope, and imaging detector and spectrometer. The inset illustrates the two different sample configurations that were explored; red arrows correspond to the input polarization directions and black arrows depict the propagation vector. |
Abstract:
Using ultra-low input power densities, researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have demonstrated for the first time how low-power "optical nanotweezers" can be used to trap, manipulate, and probe nanoparticles, including fragile biological samples.
Newly demonstrated capabilities of low-powered nanotweezers may benefit cellular-level studies
Urbana, IL | Posted on September 17th, 2012"We already know that plasmonic nanoantennas enhance local fields by up to several orders of magnitude, and thus, previously showed that we can use these structures with a regular CW laser source to make very good optical tweezers," explains, Kimani Toussaint, Jr., assistant professor of mechanical science and engineering at Illinois. "This is exciting because, for the first time, we're showing that, the near-field optical forces can be enhanced even further, without doing anything extra in terms of fabrication, but rather simply by exploiting the high-peak powers associated with using a femtosecond (fs) optical source.
"We used an average power of 50 microwatts to trap, manipulate, and probe nanoparticles. This is 100x less power than what you would get from a standard laser pointer."
In their recent paper, "Femtosecond-pulsed plasmonic nanotweezers" published in the September 17 issue of Scientific Reports; doi:10.1038/srep00660), the researchers describe how a femtosecond-pulsed laser beam significantly augments the trapping strength of Au bowtie nanoantennas arrays (BNAs), and the first demonstration of use of femtosecond (fs) source for optical trapping with plasmonic nanotweezers.
"Our system operates at average power levels approximately three orders of magnitude lower than the expected optical damage threshold for biological structures, thereby making this technology very attractive for biological (lab-on-a-chip) applications such as cell manipulation," added Toussaint, who is also an affiliate faculty member in the Department of Bioengineering and the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. "This system offers increased local diagnostic capabilities by permitting the probing of the nonlinear optical response of trapped specimens, enabling studies of in vitro fluorescent-tagged cells, or viruses using a single line for trapping and probing rather than two or more laser lines."
"We present strong evidence that a fs source could actually augment the near-field optical forces produced by the BNAs, and most likely, other nanoantenna systems, as well. To our knowledge, this has never been demonstrated," said Brian Roxworthy, a graduate student in Toussaint's PROBE (Photonics Research of Bio/nano Environments) lab group and first author of the paper. According to Roxworthy, the demonstration of controlled particle fusing could be important for creating novel nanostructures, as well as for enhancing the local magnetic field response, which will be important for the field of magnetic plasmonics.
The paper also demonstrated enhancement of trap stiffness of up to 2x that of a comparable continuous-wave (CW) nanotweezers and 5x that of conventional optical tweezers that employ a fs source; successful trapping and tweezing of spherical particles ranging from 80-nm to 1.2-um in diameter, metal, dielectric, and both fluorescent and non- fluorescent particles; enhancement of two-photon fluorescent signal from trapped microparticles in comparison to the response without the presence of the BNAs; enhancement of the second-harmonic signal of ~3.5x for the combined nanoparticle-BNA system compared to the bare BNAs; and fusing of Ag nanoparticles to the BNAS.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kimani C. Toussaint, Jr.
Department of Mechanical Science & Engineering
217/244-4088
Rick Kubetz
Engineering Communications Office
217/244-7716
writer/editor
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Copyright © University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








