Home > Press > Nanoengineers can print 3D microstructures in mere seconds
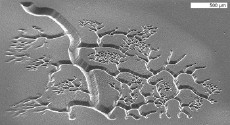 |
| NanoEngineering Professor Shaochen Chen has demonstrated the capability of printing three-dimensional blood vessels in mere seconds out of soft, biocompatible hydrogels. Being able to print blood vessels is essential to achieving the promise of regenerative medicine because it is how the body distributes oxygen and nutrients. Image Credit: Biomedical Nanotechnology Laboratory, Chen Research Group, UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering. |
Abstract:
Nanoengineers at the University of California, San Diego have developed a novel technology that can fabricate, in mere seconds, microscale three dimensional (3D) structures out of soft, biocompatible hydrogels. Near term, the technology could lead to better systems for growing and studying cells, including stem cells, in the laboratory. Long-term, the goal is to be able to print biological tissues for regenerative medicine. For example, in the future, doctors may repair the damage caused by heart attack by replacing it with tissue that rolled off of a printer.
Nanoengineers can print 3D microstructures in mere seconds
San Diego, CA | Posted on September 13th, 2012 Reported in the journal Advanced Materials, the biofabrication technology, called dynamic optical projection stereolithography (DOPsL), was developed in the laboratory of NanoEngineering Professor Shaochen Chen. Current fabrication techniques, such as photolithography and micro-contact printing, are limited to generating simple geometries or 2D patterns. Stereolithography is best known for its ability to print large objects such as tools and car parts. The difference, says Chen, is in the micro- and nanoscale resolution required to print tissues that mimic nature's fine-grained details, including blood vessels, which are essential for distributing nutrients and oxygen throughout the body. Without the ability to print vasculature, an engineered liver or kidney, for example, is useless in regenerative medicine. With DOPsL, Chen's team was able to achieve more complex geometries common in nature such as flowers, spirals and hemispheres. Other current 3D fabrication techniques, such as two-photon photopolymerization, can take hours to fabricate a 3D part.
The biofabrication technique uses a computer projection system and precisely controlled micromirrors to shine light on a selected area of a solution containing photo-sensitive biopolymers and cells. This photo-induced solidification process forms one layer of solid structure at a time, but in a continuous fashion. The technology is part of a new biofabrication technology that Chen is developing under a four-year, $1.5 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (R01EB012597). The Obama administration in March launched a $1 billion investment in advanced manufacturing technologies, including creating the National Additive Manufacturing Innovation Institute with $30 million in federal funding to focus on 3D printing. The term "additive manufacturing" refers to the way 3D structures are built layering very thin materials.
The Chen Research Group is focused on fabrication of nanostructured biomaterials and nanophotonics for biomedical engineering applications and recently moved into the new Structural and Materials Engineering Building, which is bringing nano and structural engineers, medical device labs and visual artists into a collaborative environment under one roof.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Catherine Hockmuth
858-822-1359
Copyright © University of California - San Diego
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
3D & 4D printing/Additive-manufacturing
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Fiber sensing scientists invent 3D printed fiber microprobe for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of tissue and even single cell February 10th, 2023
Fiber sensing scientists invent 3D printed fiber microprobe for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of tissue and even single cell February 10th, 2023
![]() 3D-printed decoder, AI-enabled image compression could enable higher-res displays December 9th, 2022
3D-printed decoder, AI-enabled image compression could enable higher-res displays December 9th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Printing/Lithography/Inkjet/Inks/Bio-printing/Dyes
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
![]() Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








