Home > Press > SPEEK low sulfonation and filter
 |
Abstract:
Membranes for high temperature nanofiltration often run into problems because the polymers that constitute the membrane either decompose or leach out and this compromises the performance of the membrane. Nanofiltration membranes usually contain charged polymers, which are used to reject particular ions or compounds in solution. One of the polymers which are often used for these membranes is SPEEK, sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone), due to its high thermal and mechanical stability. The problem, in this case, is that to introduce enough charges into the membrane, SPEEK with a high degree of sulfonation (30% or higher) is usually used, and this typically compromises its high temperature performance, and sometimes even room-temperature storage.
SPEEK low sulfonation and filter
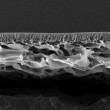
Germany | Posted on September 6th, 2012To solve these issues, Wei Yang and co-workers at Tianjin University, in a paper published in the Journal of Applied Polymer Science, have prepared a SPEEK membrane with very low degree of sulfonation, by using methylsulfonic acid as a solvent, to make it possible to prepare a membrane with a degree of sulfonation of about 7%. The advantage of this low degree of sulfonation is the good degree of thermal stability, with the onset of decomposition of the sulfonate groups starting around 350 degrees Celsius, but small weight loss due to the low degree of sulfonation.
The authors tested the membrane's nanofiltration performance using two model dyes, and showed that, up to 80 degrees Celsius, the membranes filter out 90% and 80% of each of the two dyes respectively, with flux increasing with temperature and selectivity decreasing with temperature.
While this membrane will need further study, it shows promise as a high temperature nanofiltration platform.
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Wiley-VCH Materials Science Journals
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Link to the original paper on Wiley Online Library
Link to the original paper on Wiley Online Library
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








