Home > Press > Understanding the biological and ecological implications of safe nanotechnology
 |
Abstract:
Nanoscale science and technology has seen exciting advances recently in drug delivery, electronics, energy and environmental applications. According to international scientific conventions, nanomaterials are those whose at least one dimension is less than or equal to 10-9 m. At the same time, there is a great possibility for nanomaterials to enter ecosystems at the points of use or disposal, which could lead to negative environmental implications.
Understanding the biological and ecological implications of safe nanotechnology
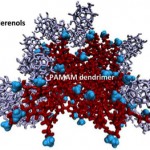
Clemson, SC | Posted on August 6th, 2012Our recent paper, "Dendrimer-fullerenol soft-condensed nanoassembly" published in The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, showed how the soft nanomaterial dendrimer can be used to remediate the environment from potentially toxic nanomaterials. Here, we used fullerenol - a 60 carbon molecule in the shape of a buckyball and functionalized with hydroxyl groups - as a model system. Such an assembly also has implications for drug delivery.
We found that the assemblies of dendrimers and fullerenols were strong, spontaneous, and thermodynamically favorable at neutral water pH and ambient temperature and pressure.
Dendrimers are highly branched, polymeric macromolecules with a high degree of surface functionalities. Their branching determines their generation number (G) - the higher the generation, the greater the degree of surface functionalities. We used both G1 and G4 poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) dendrimers and found that both these dendrimers hosted one fullerenol per primary amine on the dendrimer surfaces. However, G4 PAMAM dendrimers hosted fullerenols 40 times better than G1, simply because of their higher degree of surface functionalities. Based on our findings, we recommended proper loading capacities of fullerenols for G1 and G4 dendrimers in drug delivery and environmental remediation.
With the advent of new technologies, the public often becomes skeptical of their implications on the environment. In our group, we strive to understand the biological and ecological implications of safe nanotechnology. This article was a part of that effort. Fullerenols have shown great potential in nanomedicine as well as in electronics. Dendrimers of generations five and below have been proven biocompatible, and have been used as MRI contrast agents and drug delivery vehicles. In this paper we provided a proof-of-concept on the use of a benign dendritic technology as a robust drug delivery vehicle and a solution to environmental remediation of discharged nanomaterials.
Our group, led by my advisor Dr. Pu-Chun Ke and funded by the National Science Foundation, has delved into a crucial topic of frontier research termed "nanoparticle-protein corona". In short, nanoparticles do not interact directly with living systems but are often coated with biological fluids in the form of a protein corona. Another direction in our group, through collaboration between Dr. Ke and Dr. David Ladner in Clemson's Department of Environmental Engineering and Earth Sciences and funded by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency is to employ dendritic polymers for remediating oil spills.
Priyanka Bhattacharya is a PhD student at Clemson University's College of Engineering and Science
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Brian Mullen
864-656-2063
Copyright © Clemson University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() “Dendrimer-fullerenol soft-condensed nanoassembly” published in The Journal of Physical Chemistry C
“Dendrimer-fullerenol soft-condensed nanoassembly” published in The Journal of Physical Chemistry C
![]() Clemson University’s College of Engineering and Science
Clemson University’s College of Engineering and Science
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Safety-Nanoparticles/Risk management
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








