Home > Press > ‘Loops of light’ promising for optical detection of individual molecules
 |
Abstract:
KU Leuven researcher Ventsislav Valev and an international team of colleagues have developed a new method for manipulating light at the nanoscale in order to optically detect single molecules. By shining circularly polarised light on a gold, square-ring shaped nanostructure, the researchers were able to ‘activate' the entire surface of the nanostructure, thereby significantly increasing the opportunity for interaction with molecules. The method has a broad range of potential applications in nanoscale photochemistry and could assist in the advancement of technologies for visualising single molecules and multiple-molecule interactions.
‘Loops of light’ promising for optical detection of individual molecules
Leuven, Belgium | Posted on July 19th, 2012Nanotechnology researchers around the world are exploring ways to optically detect single molecules, but progress can be hindered by the fact that single molecules have extremely weak optical responses. Thus far, scientists have developed a way to use metal nanostructures to focus light into tiny spots called ‘hotspots'. The hotspots excite electrons on the surface of the nanostructure, causing them to oscillate coherently. When shone on a molecule, and with the help of these oscillating electrons, the focused light can increase a molecule's optical signal to 100 billion times its normal strength. This signal can then be detected with an optical microscope.
But there are two limitations to the current method: hotspots can become too hot, and they are just spots. That is, the heat from hotspots can melt the nanostructures, thus destroying their ability to channel light effectively, and hotspots produce only a very small cross-section in which interaction with molecules can take place. Additionally, for a single molecule to become detectable, it needs to find the hotspot.
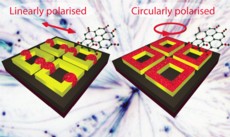
Loops of light
In order to overcome these limitations, Dr. Valev and his colleagues sought out to nanoengineer larger spots. They began by shining circularly polarised light rather than linearly polarised light on the nanostructures and found that this could increase the useful area of these nanostructures. More importantly, when shone on square-ring shaped gold nanostructures, the scientists observed that theentire surface of the nanostructures was successfully activated.
Dr. Valev explains: "Essentially, light is constituted of electric and magnetic fields moving through space. While with linearly polarised light, the fields move in a linear, forward direction, with circularly polarised light, they rotate in a spiral-like motion." The circularly polarised light imparts a sense of rotation on the electron density in ring-shaped gold nanostructures, thus trapping the light in the rings and forming ‘loops of light'. The loops of light cause excited electrons to oscillate coherently on the full surface of the square-ringed nanostructures - rather than in a few concentrated hotspots. This increases the opportunity for interaction with molecules: "The trick is to try to activate the whole surface of the nanostructure so that whenever a molecule attaches, we will be able to see it," says Dr. Valev. "That is precisely what we did."
The method has a broad range of potential applications in nanoscale photochemistry and could assist in the advancement of technologies for visualising single molecules and multiple-molecule interactions. The findings were published in the scientific journal Advanced Materials.
Full bibliographic information
Valev, V. K., De Clercq, B., Biris, C. G., Zheng, X., Vandendriessche, S., Hojeij, M., Denkova, D., Jeyaram, Y., Panoiu, N. C., Ekinci, Y., Silhanek, A. V., Volskiy, V., Vandenbosch, G. A. E., Ameloot, M., Moshchalkov, V. V. and Verbiest, T. (2012), Distributing the Optical Near-Field for Efficient Field-Enhancements in Nanostructures. Advanced Materials doi: 10.1002/adma.201201151
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ventsislav Valev
Molecular Imaging and Photonics
KU Leuven
+32 16 3 27622
Copyright © AlphaGalileo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








