Home > Press > Graphene-control cutting using an atomic force microscope-based nanorobot
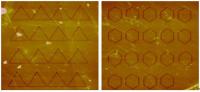 |
| This shows graphene cutting results based on a nanorobot.
Credit: ©Science China Press |
Abstract:
Graphene, a stable two-dimensional structure, has attracted tremendous worldwide attention in recent years because of its unique electronic, physical and mechanical properties as well as its wide range of applications. It has been proven experimentally that the electrical properties of graphene are strongly related to its size, geometry, and edge structure. Therefore, controlling graphene to desired edge structures and shapes is required for its practical application. To date, researchers have explored many graphene patterning methods, such as a catalytic cutting [1-4], SPM(Scanning Probe Microscopy)-based electric field tailoring [5-7], energy beam cutting [8-10] and photocatalytic patterning techniques [11]. The current methods can tailor graphene, however, lack of real-time sensor feedback during patterning and cutting results in an open-loop manufacturing process. This greatly limits the cutting precision of graphene and reduces the efficiency of device manufacture. Therefore, a closed-loop fabrication method using interaction forces as real-time feedback is needed to tailor graphene into desired edge structures and shapes in a controllable manner.
Graphene-control cutting using an atomic force microscope-based nanorobot
PR China | Posted on May 27th, 2012Professor LIU Lianqing from the State Key Laboratory of Robotics, Shenyang Institute of Automation Chinese Academy of Sciences and Professor XI Ning from the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Michigan State University undertook the background research to overcome this challenge. Their work, entitled "Graphene Control Cutting Using an Atomic Force Microscope Based NanoRobot", was published in SCIENTIA SINICA Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica. 2012, Vol 42(4). They investigated controlled cutting methods of graphene based on nanoscale force feedback by the introduction of robot perception, drivers and behavior coupled with an atomic force microscope. They found that the cutting forces were related to the cutting direction of the graphene lattice because of the asymmetry of the crystal structure of graphene. This discovery is expected to allow nanoscale forces to be used as real-time feedback to establish a closed-loop mechanism to cut graphene with precise control.
Atomic force microscopy is only a nanoscale observation tool, and its main shortcomings are poor location ability, lack of real-time feedback, and low efficiency. These challenges are solved by the introduction of robotics that is efficient at nanomanipulation. In this article, the relationship between lattice cutting directions and nanocutting forces were studied systematically by rotating the sample under the same cutting conditions (load, cutting velocity, tip, and effective cutting surface of the tip). The experimental results show that the cutting force is related to the lattice cutting direction: the cutting forces vary with cutting direction in the same period with a difference of up to around 209.36 nN.
This article is the first to show that cutting forces vary with lattice cutting directions, which lays an experimental foundation to build a closed-loop fabrication strategy using real-time force as a sensor feedback to control the cutting direction with lattice precision. Combined with existing parallel multi-tip technology, the technique developed in this work will make it possible to fabricate large-scale graphene-based nanodevices at low cost with high efficiency. This research was supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2009AA03Z316), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project Nos. 60904095, 51050110445, and 61175103), and the CAS/SAFEA (Chinese Academy of Sciences/State Administration of Foreign Experts Affairs) International Partnership Program for Creative Research Teams.
See the article: Zhang Y, Liu L Q, Xi N, et al. Graphene Control Cutting Using an Atomic Force Microscope Based NanoRobot (In Chinese). SCIENTIA SINICA Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica, 2012, 42(4):358
References
[1] Datta, S S.et al. Crystallographic Etching of Few-Layer Graphene. Nano Lett, 8, 1912-1915 (2008).
[2] Ci, L. et al. Controlled nanocutting of graphene. Nano Research, 1, 116-122 (2008).
[3] Campos, L. C. et al. Anisotropic Etching and Nanoribbon Formation in Single-Layer Graphene. Nano Lett, 9, 2600-2604 (2009).
[4] Gao, L. et al. Crystallographic Tailoring of Graphene by Nonmetal SiOx Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc, 131, 13934-13936 (2009).
[5] Giesbers, A. J. M. et al. Nanolithography and manipulation of graphene using an atomic force microscope. Sol. St. Comm, 147, 366-369 (2008).
[6] Tapaszto, L., Dobrik, G., Lambin, P. & Biro, L. P. Tailoring the atomic structure of graphene nanoribbons by scanning tunnelling microscope lithography. Nat Nano, 3, 397-401 (2008).
[7] Weng, L., Zhang, L.Y., Chen, Y. P. & Rokhinson L.P. et al. Atomic force microscope local oxidation nanolithography of graphene. Appl. Phys. Lett, 93, 093107 (2008)
[8] Fischbein, M. D. & Drndic, M. Electron beam nanosculpting of suspended graphene sheets. Appl. Phys. Lett, 93, 113107 (2008).
[9] Bell, D. C., Lemme, M. C., Stern, L. A. & Marcus, C. M. Precision cutting and patterning of graphene with helium ions. Nanotechnology, 20, 455301(2009).
[10] Lemme, M. C., Bell, D. C., Williams, J. R. Etching of Graphene Devices with a Helium Ion Beam. ACS Nano, 3, 2674-2676(2009).
[11] Zhang, L.M., et al. Photocatalytic Patterning and Modification of Graphene. J. Am. Chem.Soc. 133, 2706-2713(2011)
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
LIU Lianqing
Copyright © Science in China Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








