Home > Press > Purdue professor to speak before Congress about nanotechnology in brain treatment research
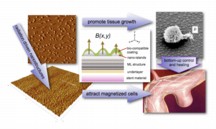 |
| This diagram illustrates the concept behind a new type of "bioactive" coating for stents used to treat brain aneurisms, including those suffered by military personnel from head trauma due to bomb blasts. Portions of the stents - tubular structures made of a metallic mesh - will be designed using coatings to attract magnetized cells to repair blood vessels damaged in trauma. (Purdue University image/Jean Paul Allain) |
Abstract:
Researchers at Purdue University are working with the U.S. Army and neurosurgeons at the Walter Reed National Military Medical Center to create a new type of "bioactive" coating for stents used to treat brain aneurisms including those caused by head trauma from bomb blasts.
Purdue professor to speak before Congress about nanotechnology in brain treatment research
West Lafayette, IN | Posted on May 21st, 2012"Stents coated with a bioactive coating might be inserted at the site of an aneurism to help heal the inside lining of the blood vessel," said Jean Paul Allain, an associate professor of nuclear engineering. "Aneurisms are saclike bulges in blood vessels caused by weakening of artery walls. We're talking about using a regenerative approach, attracting cells to reconstruct the arterial wall."
He will speak before Congress on Thursday (May 24) during the first Brain Mapping Day to discuss the promise of nanotechnology in treating brain injury and disease.
Purdue researchers are working with Col. Rocco Armonda, Dr. Teodoro Tigno and other neurosurgeons at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center in Bethesda, Md. Collaborations also are planned with research scientists from the University of Queensland in Australia, Universidad de Antioquía and Universidad de Los Andes, both in Colombia.
Portions of the stents - tubular structures made of a metallic mesh - will be designed using bioactive coatings to attract magnetized cells to repair blood vessels damaged in trauma.
The stent coatings are modified in a Purdue facility that uses beams of charged particles called ions to modify the stent coatings with a magnetic material. The ion beams also are used to create lifelike or "biomimetic" surface textures designed to promote cellular proliferation and repair damaged vessels, Allain said.
Findings will be detailed in an invited talk to be delivered by Allain during the Ninth Annual World Congress of SBMT on Brain, Spinal Cord Mapping and Image Guide Therapy on June 2-4 in Toronto.
Currently, aneurisms are treated either by performing brain surgery, opening the skull and clipping the sac, or by inserting a catheter through an artery into the brain and implanting a metallic coil into the balloon-like sac.
Both procedures risk major complications, including massive bleeding or the formation of potentially fatal blood clots.
"The survival rate is about 50/50 or worse, and those who do survive could be impaired," said Allain, who holds a courtesy appointment with materials engineering and is affiliated with the Birck Nanotechnology Center in Purdue's Discovery Park.
Cells needed to repair blood vessels are influenced by both the surface texture - features such as bumps and irregular shapes as tiny as 10 nanometers wide - as well as the surface chemistry of the stent materials.
"We are learning how to regulate cell proliferation and growth by tailoring both the function of surface chemistry and topology," Allain said. "There is correlation between surface chemistry and how cells send signals back and forth for proliferation. So the surface needs to be tailored to promote regenerative healing."
The facility being used to irradiate the stents - the Radiation Surface Science and Engineering Laboratory in Purdue's School of Nuclear Engineering - also is used for work aimed at developing linings for experimental nuclear fusion reactors for power generation.
Irradiating materials with the ion beams causes surface features to "self-organize" and also influences the surface chemistry, Allain said.
The stents are made of nonmagnetic materials, such as stainless steel and an alloy of nickel and titanium. Only a certain part of the stents is rendered magnetic to precisely direct the proliferation of cells to repair a blood vessel where it begins bulging to form the aneurism.
Researchers will study the stents using blood from pigs during the first phase in collaboration with the Walter Reed National Military Medical Center.
The stent coating's surface is "functionalized" so that it interacts properly with the blood-vessel tissue. Some of the cells are magnetic naturally, and "magnetic nanoparticles" would be injected into the bloodstream to speed tissue regeneration. Researchers also are aiming to engineer the stents so that they show up in medical imaging to reveal how the coatings hold up in the bloodstream.
The research is led by Allain and co-principal investigator Lisa Reece of the Birck Nanotechnology Center. This effort has spawned new collaborations with researchers around the world including those at Universidad de Antioquía, University of Queensland. The research also involves doctoral students Ravi Kempaiah and Emily Walker.
The work is funded with a three-year, $1.5 million grant from the U.S. Army.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Writer: Emil Venere
765-494-4709
Source:
Jean Paul Allain
765 496-9718
Copyright © Purdue University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Events/Classes
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
![]() A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks January 20th, 2023
Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks January 20th, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








