Home > Press > Perfectly spherical gold nanodroplets produced with the smallest-ever nanojets
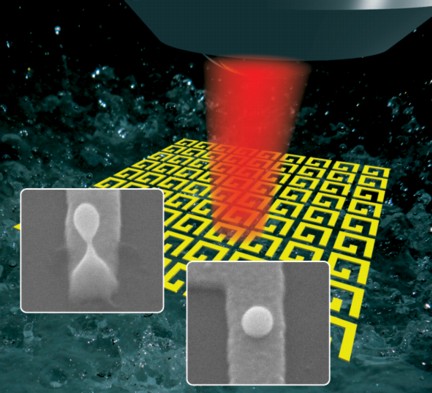 |
| Similar to the way water backjets eject droplets of water on the surface of a pond, powerful laser pulses can locally melt gold nanostructures and produce gold nanojets, ejecting perfectly spherical gold nanodroplets. |
Abstract:
KU Leuven researcher Ventsislav Valev and an international team of scientists have developed a new method for optical manipulation of matter at the nanoscale. Using ‘plasmonic hotspots' - regions with electric current that heat up very locally - gold nanostructures can be melted and made to produce the smallest nanojets ever observed. The tiny gold nanodroplets formed in the nanojets, are perfectly spherical, which makes them interesting for applications in medicine.
Perfectly spherical gold nanodroplets produced with the smallest-ever nanojets
Leuven, Belgium | Posted on January 14th, 2012The ‘backjet' phenomenon on which the method turns can be compared to a pebble being dropped into water. Tightly focused ultrafast laser pulses carry sufficient energy to locally melt the surface of a gold film. When a laser pulse of light hits the film, a nanoscale backjet - a nanojet - of molten gold surges upward.
As the name suggests, nanojets on the surface of a homogeneous gold film are incredibly small, their size being determined by the distribution of energy in the light pulse. This distribution of energy is in turn dependent on the wavelength of light. Initially, scientists anticipated that nanojets could not be significantly smaller than the wavelength of light. In this study however, Ventsislav Valev and his colleagues show that nanojets can in fact be made much smaller with the help of ‘plasmonic hotspots'.
Plasmonic hotspots are regions on the surface of metal nanostructures where light causes very strong oscillation of the electrons. Because electron oscillations constitute an electric current and because electric currents heat up the material the same way an electric stove heats up in the kitchen, the plasmonic hotspots are extremely hot. So hot that they can melt the gold in a spot much smaller than the wavelength of light. Dr. Valev and his colleagues were successfully able to demonstrate that this tiny little pool of molten gold can give rise to the smallest nanojets ever observed.
The gold nanodroplets propelled upward by the nanojets solidify in flight, producing perfectly spherical nanoparticles. These gold nanodroplets can be collected and used for medical applications including cancer treatment. The nanoparticles can be attached to molecules and injected in the blood. Once the molecules attach to cancer cells, light can be used to heat up the gold nanodroplets and destroy the cancer cells. Currently, the gold nanoparticles used in medications are chemically synthesised. These chemically synthesised gold nanoparticles have an unavoidably granular aspect. Conversely, gold nanodroplets created by the plasmonic nanojet method detailed by Dr. Valev and his colleagues are perfectly spherical, ensuring a better efficiency.
The study was conducted in collaboration with scientists from Germany, the United Kingdom, Bulgaria, Russia and Singapore and is published in the latest edition of the journal Advanced Materials.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Ventsislav Valev
Molecular Imaging and Photonics
Faculty of Science
University of Leuven
Griet Van der Perre
+32 16 32 40 08
Copyright © AlphaGalileo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








