Home > Press > Now you see it, now you didn't: Cloaking a moment in time
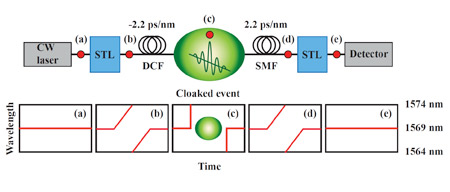 |
| A laser beam passes through a "split-time lens" - a specially designed waveguide that bumps up the wavelength for a while then suddenly bumps it down. The signal then passes through a filter that slows down the higher-wavelength part of the signal, creating a gap in which the cloaked event takes place. A second filter works in the opposite way from the first, letting the lower wavelength catch up, and a final split-time lens brings the beam back to the original wavelength, leaving no trace of what happened during the gap. |
Abstract:
In movie magic, people and objects can appear or disappear or move from place to place in an instant. Just stop the camera, move things around and start it again. Now, Cornell researchers have demonstrated a similar "temporal cloak" -- albeit on a very small scale -- in the transport of information by a beam of light.
Now you see it, now you didn't: Cloaking a moment in time
Ithaca, NY | Posted on January 5th, 2012The trick is to create a gap in the beam of light, have the hidden event occur as the gap goes by and then stitch the beam back together. Alexander Gaeta, professor of applied and engineering physics, and colleagues report their work in the Jan. 5 issue of the journal Nature.
The researchers created what they call a time lens, which can manipulate and focus signals in time, analogous to the way a glass lens focuses light in space. They use a technique called four-wave mixing, in which two beams of light, a "signal" and a "pump," are sent together through an optical fiber. The two beams interact and change the wavelength of the signal. To begin creating a time gap, the researchers first bump the wavelength of the signal up, then by flipping the wavelength of the pump beam, bump it down.
The beam then passes through another, very long, stretch of optical fiber. Light passing through a transparent material is slowed down just a bit, and how much it is slowed varies with the wavelength. So the lower wavelength pulls ahead of the higher, leaving a gap, like the hare pulling ahead of the tortoise. During the gap the experimenters introduced a brief flash of light at a still higher wavelength that would cause a glitch in the beam coming out the other end.
Then the split beam passes through more optical fiber with a different composition, engineered to slow lower wavelengths more than higher. The higher wavelength signal now catches up with the lower, closing the gap. The hare is plodding through mud, but the tortoise is good at that and catches up. Finally, another four-wave mixer brings both parts back to the original wavelength, and the beam emerges with no trace that there ever was a gap, and no evidence of the intruding signal.
None of this will let you steal the crown jewels without anyone noticing. The gap created in the experiment was 15 picoseconds long, and might be increased up to 10 nanoseconds, Gaeta said. But the technique could have applications in fiber-optic data transmission and data processing, he added. For example, it might allow inserting an emergency signal without interrupting the main data stream, or multitasking operations in a photonic computer, where light beams on a chip replace wires.
The experiment was inspired, Gaeta said, by a theoretical proposal for a space-time cloak or "history editor" published by Martin McCall, professor of physics at Imperial College in London, in the Journal of Optics in November 2010.
"But his method required an optical response from a material that does not exist," Gaeta said. "Now we've done it in one spatial dimension. Extending it to two [that is, hiding a moment in an entire scene] is not out of the realm of possibility. All advances have to start from somewhere."
The research was funded by the Defense Advanced Research Project Agency and by Cornell's Center for Nanoscale Systems, which is supported by the National Science Foundation and the New York State Division of Science, Technology and Innovation (NYSTAR).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact:
Blaine Friedlander
(607) 254-8093
Cornell Chronicle:
Bill Steele
(607) 255-7164
Copyright © Cornell University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








