Home > Press > Trojan Horse Causes Nanoparticle Allergy
 |
Abstract:
Workers with existing allergic conditions have worse reactions when exposed to nanoparticles in the workplace, suggest Chinese scientists. They believe that the response is caused by a Trojan horse known as an exosome, which is present in all of us.
Trojan Horse Causes Nanoparticle Allergy
Germany | Posted on December 18th, 2011Nanoparticles are becoming ubiquitous in industry and commercial applications, and there are rightly concerns about their safety, which is often still not as well understood as their physical properties. In particular, it is important for employers to understand the effects of nanoparticles on the immune system and allergic reactions to them in order to safeguard their workers against long-term and short-term effects of exposure.
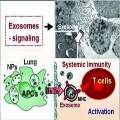
Now, a team of scientists at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, led by Guangjun Nie and Yuliang Zhao, has studied these effects using magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. They propose that, when inhaled, the nanoparticles induce formation of a vesiclelike intra- and intercellular vehicle called an exosome in the lungs. Inhalation is the most common way for nanoparticles to be introduced to the human body. Exosomes are known to act as Trojan horses to deliver sometimes unwanted particles such as viruses into cells, and in this case they quickly remove the nanoparticles from the lungs and convey signals throughout the body, including to the immune system. In those individuals that already have some kind of allergic respiratory condition (known as sensitized individuals), these signals can result in both direct and indirect activation of T cells, which cause familiar allergic responses such as inflammation. In unsensitized individuals the body's response is much lower, as the pathway to T-cell activation only takes the indirect pathway.
The scientists believe that their work should urgently inform policy guidelines and further research to protect both sensitized and unsensitized workers from allergic reactions caused by occupational exposure to nanoparticles.
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() M. Zhu et al., Small ; DOI: 10.1002/smll.201101708
M. Zhu et al., Small ; DOI: 10.1002/smll.201101708
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Safety-Nanoparticles/Risk management
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








