Home > Press > Novel Gold-Nanoparticle-Based Assay for Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease
 |
Abstract:
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is an enzyme that can catalytically break down acetylcholine at cholinergic synapses, resulting in the termination of synaptic transmission. It had been shown that the level of AChE in the cerebrospinal fluid of individuals suffering from Alzheimer's disease is significantly reduced. Therefore, a low level of AChE may indicate a risk or a preclinical stage of Alzheimer's disease. This information could be useful for early prevention and treatment of the disease. However, to date there is no accurate method for identifying Alzheimer's disease in an early or asymptomatic stage of the disease.
Novel Gold-Nanoparticle-Based Assay for Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease
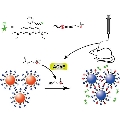
Germany | Posted on December 13th, 2011The clinical application of existing gold nanoparticle (AuNP)-based colorimetric assays is hampered by their moderate sensitivity and selectivity. Now, however, Xingyu Jiang and co-workers (National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing) have developed a novel AuNP-based assay highly sensitive to acetylcholinesterase (AChE). The fluorescence of Rhodamine B detached from Au surfaces is measured and simultaneously the color change of AuNPs solutions is known.
This new assay provides a detection limit (0.1 mU/mL) much lower than that of all existing probes for AChE. Such a high sensitivity allows the measurement of AChE in the cerebrospinal fluid even after being diluted more than a thousand times. In this manner, false positive results for other components like biothiols in real samples can be ruled out and relevant clinical tests are rendered possible. The study shows that the level of AChE in model mice that suffer from Alzheimer's disease (AD) is lower than that in healthy mice. The assay also allows the progression of the disease and the effect of drug treatments to be studied by monitoring the AChE level in the model mice treated with different drug dosages.
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Wiley-VCH Materials Science Journals
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Dingbin Liu et al., Adv. Healthcare Mat. ; DOI: 10.1002/adhm.201100002
Dingbin Liu et al., Adv. Healthcare Mat. ; DOI: 10.1002/adhm.201100002
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








