Home > Press > Fighting Parkinson's with carbon nanoparticles
 |
Abstract:
One of the problems affecting the human nervous system is dopamine deficiency. But testing of dopamine concentration is costly and requires sophisticated equipment not available in a doctor's office. Enter a team of Polish scientists who developed a method enabling the detection of dopamine in solutions both easily and cheaply, even in the presence of interferences. The study is an outcome of the NOBLESSE ('Nanotechnology, biomaterials and alternative energy source for the European Research Area (ERA))' project, which is backed with EUR 3.3 million under the 'Regions of Knowledge' Theme of the EU's Seventh Framework Programme (FP7). The results are published in the journal Biosensors and Bioelectronics.
Fighting Parkinson's with carbon nanoparticles
Warsaw, Poland | Posted on November 28th, 2011Scientists at the Institute of Physical Chemistry of the Polish Academy of Sciences (IPC PAS) in Warsaw coated new electrodes with carbon nanoparticles deposited on silicate submicroparticles to get the targeted result. They applied the electrodes so as to determine dopamine concentration in solutions in the presence of uric and ascorbic acids, and paracetamol, substances that get in the way of dopamine analysis.
This latest development to detect dopamine could clear the path for securing fast and inexpensive medical tests that doctors can use even in their offices. This information will help physicians determine the likelihood of a patient suffering from popular nervous system disorders including Parkinson's disease.
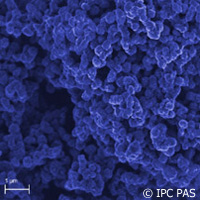
The researchers developed the electrodes by alternating layers of silicate submicroparticles and carbon nanoparticles. According to the team, the size of the silicate submicroparticles ranges from 100 nanometres to 300 nanometres (billionth parts of a metre). Being nonconductive, they are used only as a framework extending the electrode surface. Carbon nanoparticles, ranging between 8 nanometres and 18 nanometres in size, densely coat the silicate particles that form the actual conductive working surface.
'Carbon nanoparticles have negatively charged functional groups, and the silicates positively charged ones,' explains doctoral student Anna Celebanska of the IPC PAS. 'The electrostatic interactions between them are quite strong. We checked that by multiple repeating of the immersion, a "sandwich" consisting of up to 24 layers can be obtained on the electrode surface.'
The scientists applied the new electrodes for dopamine sensing in solutions. The carbon nanoparticle-coated electrodes are placed inside a prepared solution containing the same, and the electric potential is then applied. They say dopamine is electrochemically active and can be oxidised by adjusting the potential value.
'The results of the completed tests turned out very good,' Ms Celebanska says. 'Our method is among the most sensitive methods for dopamine sensing. It allows to detect dopamine at concentrations as low as 10-7 mole per litre in the presence of interferences at concentrations up to 10-3 mole per litre.'
Commenting on the results of the study, Professor Marcin Opallo [z1]says: 'The method has a natural detection threshold, and that's why we can conclude on dopamine deficiency in the body. How large is the actual deficiency? At present we cannot answer the question. We hope, however, for further increase in the method's sensitivity.'
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Cordis
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Institute of Physical Chemistry of the Polish Academy of Sciences (IPC PAS):
Institute of Physical Chemistry of the Polish Academy of Sciences (IPC PAS):
![]() Biosensors and Bioelectronics:
Biosensors and Bioelectronics:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








