Home > Press > Carbon nanotube forest camouflages 3-D objects
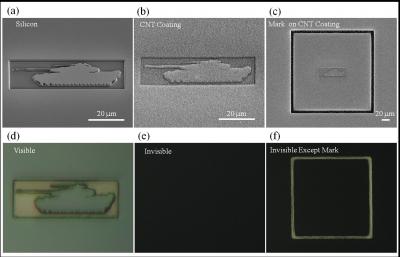 |
| Scanning electron microscope images show a tank etched out of silicon, with and without a carbon nanotube coating (top row). When the same structures are viewed under white light with an optical microscope (bottom row), the nanotube coating camouflages the tank structure against a black background.
Credit: L. J. Guo et al, University of Michigan/Applied Physics Letters |
Abstract:
Carbon nanotubes, tiny cylinders composed of one-atom-thick carbon lattices, have gained fame as one of the strongest materials known to science. Now a group of researchers from the University of Michigan is taking advantage of another one of carbon nanotubes' unique properties, the low refractive index of low-density aligned nanotubes, to demonstrate a new application: making 3-D objects appear as nothing more than a flat, black sheet.
Carbon nanotube forest camouflages 3-D objects
College Park, MD | Posted on November 21st, 2011The refractive index of a material is a measure of how much that material slows down light, and carbon nanotube "forests" have a low index of refraction very close to that of air. Since the two materials affect the passage of light in similar ways, there is little reflection and scattering of light as it passes from air into a layer of nanotubes.
The Michigan team realized they could use this property to visually hide the structure of objects. As described in the AIP's journal Applied Physics Letters, the scientists manufactured a 3-D image of a tank out of silicon. When the image was illuminated with white light, reflections revealed the tank's contours, but after the researchers grew a forest of carbon nanotubes on top of the tank, the light was soaked up by the tank's coating, revealing nothing more than a black sheet.
By absorbing instead of scattering light, carbon nanotube coatings could cloak an object against a black background, such as that of deep space, the researchers note. In such cases the carbon nanotube forest "acts as a perfect magic black cloth that can completely conceal the 3-D structure of the object," the researchers write.
Article: "Low density carbon nanotube forest as an index-matched and near perfect absorption coating" is accepted for publication in Applied Physics Letters.
Authors: Haofei Shi (1), Jong G. Ok (2), Hyoung Won Baac, (1) and L. Jay Guo (1).
(1) Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, University of Michigan
(2) Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Michigan
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Catherine Meyers
301-209-3088
Copyright © American Institute of Physics
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








