Home > Press > Stanford engineers use nanophotonics to reshape on-chip computer data transmission: New nanoscale light-emitting diode is thousands of times more energy efficient that laser-based devices and ultrafast; could transform computer data transmission at the chip level
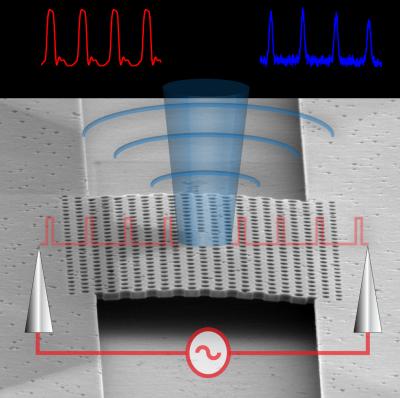 |
| This illustration shows how a single nanophotonic single-mode LED is constructed.
Credit: Gary Shambat, Stanford School of Engineering |
Abstract:
A team at Stanford's School of Engineering has demonstrated an ultrafast nanoscale light emitting diode (LED) that is orders of magnitude lower in power consumption than today's laser-based systems and able to transmit data at 10 billion bits per second. The researchers say it is a major step forward in providing a practical ultrafast, low-power light sources for on-chip computer data transmission.
Stanford engineers use nanophotonics to reshape on-chip computer data transmission: New nanoscale light-emitting diode is thousands of times more energy efficient that laser-based devices and ultrafast; could transform computer data transmission at the chip level
Stanford, CA | Posted on November 15th, 2011Stanford's Jelena Vuckovic, an associate professor of electrical engineering and the study's senior author, and first author Gary Shambat, a doctoral candidate in electrical engineering, announced their device in paper to be published November 15 in the journal Nature Communications.
Vuckovic had earlier this year produced a nanoscale laser that was similarly efficient and fast, but that device operated only at temperatures below 150 Kelvin, about 190 degrees below zero Fahrenheit, making them impractical for commercial use. The new device operates at room temperature and could, therefore, represent an important step toward next-generation computer processors.
"Low-power, electrically controlled light sources are vital for next generation optical systems to meet the growing energy demands of the computer industry," said Vuckovic. "This moves us in that direction significantly."
Single-Mode Light
The LED in question is a "single-mode LED," a special type of diode that emits light more or less at a single wavelength, very similar to a laser.
"Traditionally, engineers have thought only lasers can communicate at high data rates and ultralow power," said Shambat. "Our nanophotonic, single-mode LED can perform all the same tasks as lasers, but at much lower power."
Nanophotonics is key to the technology. In the heart of their device, the engineers have inserted little islands of the material indium arsenide, which, when pulsed with electricity, produce light. These islands are surrounded by photonic crystal - an array of tiny holes etched in a semiconductor. The photonic crystal serves as a mirror that bounces the light toward the center of the device, confining it inside the LED and forcing it to resonate at a single frequency.
"In other words, the light becomes single-mode," said Shambat.
"Without these nanophotonic ingredients - the 'quantum dots' and the photonic crystal - it is impossible to make an LED efficient, single-mode and fast all at the same time," said Vuckovic.
Engineering Ingenuity
The new device includes a bit of engineering ingenuity, too. Existing devices are actually two devices, a laser coupled with an external modulator. Both devices require electricity. Vuckovic's diode combines light emission and modulation functions into one device that drastically reduces energy consumption.
On average, the new LED device transmits data at 0.25 femto-Joules per bit of data. By comparison, today's typical 'low' power laser device requires about 500 femto-Joules to transmit a single bit. Some technologies consume as much as one pico-Joule per bit.
"Our device is 2000 to 4000 times more energy efficient than best devices in use today" said Vuckovic.
Stanford Professor James Harris, former PhD student Bryan Ellis, and doctoral candidates Arka Majumdar, Jan Petykiewicz and Tomas Sarmiento also contributed to this research.
This article was written by Andrew Myers, the associate director of communications at the Stanford School of Engineering.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Andrew Myers
650-736-2241
Copyright © Stanford School of Engineering
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








