Home > Press > New hybrid technology could bring 'quantum information systems'
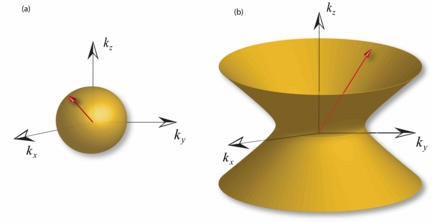 |
| Structures called "metamaterials" and the merging of two technologies under development are promising the emergence of new "quantum information systems" far more powerful than today's computers. The concept hinges on using single photons – the tiny particles that make up light – for switching and routing in future computers that might harness the exotic principles of quantum mechanics. The image at left depicts a "spherical dispersion" of light in a conventional material, and the image at right shows the design of a metamaterial that has a "hyperbolic dispersion" not found in any conventional material, potentially producing quantum-optical applications. (Zubin Jacob) |
Abstract:
The merging of two technologies under development - plasmonics and nanophotonics - is promising the emergence of new "quantum information systems" far more powerful than today's computers.
New hybrid technology could bring 'quantum information systems'
West Lafayette, IN | Posted on October 27th, 2011The technology hinges on using single photons - the tiny particles that make up light - for switching and routing in future computers that might harness the exotic principles of quantum mechanics.
The quantum information processing technology would use structures called "metamaterials," artificial nanostructured media with exotic properties.
The metamaterials, when combined with tiny "optical emitters," could make possible a new hybrid technology that uses "quantum light" in future computers, said Vladimir Shalaev, scientific director of nanophotonics at Purdue University's Birck Nanotechnology Center and a distinguished professor of electrical and computer engineering.
The concept is described in an article to be published Friday (Oct. 28) in the journal Science. The article will appear in the magazine's Perspectives section and was written by Shalaev and Zubin Jacob, an assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering at the University of Alberta, Canada.
"A seamless interface between plasmonics and nanophotonics could guarantee the use of light to overcome limitations in the operational speed of conventional integrated circuits," Shalaev said.
Researchers are proposing the use of "plasmon-mediated interactions," or devices that manipulate individual photons and quasiparticles called plasmons that combine electrons and photons.
One of the approaches, pioneered at Harvard University, is a tiny nanowire that couples individual photons and plasmons. Another approach is to use hyperbolic metamaterials, suggested by Jacob; Igor Smolyaninov, a visiting research scientist at the University of Maryland; and Evgenii Narimanov, an associate professor of electrical and computer engineering at Purdue. Quantum-device applications using building blocks for such hyperbolic metamaterials have been demonstrated in Shalaev's group.
"We would like to record and read information with single photons, but we need a very efficient source of single photons," Shalaev said. "The challenge here is to increase the efficiency of generation of single photons in a broad spectrum, and that is where plasmonics and metamaterials come in."
Today's computers work by representing information as a series of ones and zeros, or binary digits called "bits."
Computers based on quantum physics would have quantum bits, or "qubits," that exist in both the on and off states simultaneously, dramatically increasing the computer's power and memory. Quantum computers would take advantage of a strange phenomenon described by quantum theory called "entanglement." Instead of only the states of one and zero, there are many possible "entangled quantum states" in between one and zero.
An obstacle in developing quantum information systems is finding a way to preserve the quantum information long enough to read and record it. One possible solution might be to use diamond with "nitrogen vacancies," defects that often occur naturally in the crystal lattice of diamonds but can also be produced by exposure to high-energy particles and heat.
"The nitrogen vacancy in diamond operates in a very broad spectral range and at room temperature, which is very important," Shalaev said.
The work is part of a new research field, called diamond photonics. Hyperbolic metamaterials integrated with nitrogen vacancies in diamond are expected to work as efficient "guns" of single photons generated in a broad spectral range, which could bring quantum information systems, he said.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Writer:
Emil Venere
765-494-4709
Sources:
Vladimir Shalaev
765-494-9855
Zubin Jacob
Copyright © Purdue University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








