Home > Press > Bone Marrow Gets Targeted Drug Delivery
 |
Abstract:
Bone marrow, the spongy, flexible tissue found in the center of bones, is essential for the production of blood cells. There are multiple diseases and infections that involve the bone marrow, but current strategies to treat these disorders involve intravenous delivery of drugs are not specifically targeted to the diseased marrow. The healthy cells in the body are also affected, leading to toxic side effects. Thus, there is an urgent need to develop targeted drug delivery strategies to diseased cells in the bone marrow.
Bone Marrow Gets Targeted Drug Delivery
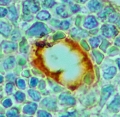
Germany | Posted on August 19th, 2011Recently, efforts in development of targeted drug delivery has heavily involved nanotechnology, which uses the strategy of active targeting. Porous silicon is an attractive material because of its biocompatibility and ability to carry various agents, from proteins to drugs and nanoparticles. In a new study featured in Advanced Healthcare Materials, Mauro Ferrari, David Gorenstein and their colleagues developed a system comprising nanoporous silicon particles and a cell adhesion molecule that specifically targets bone marrow and delivers a high amount of nanoparticles containing therapeutic drugs to the bone marrow tissue. The cell adhesion molecule, E-selectin, has recently shown promise as a biological target for the delivery of drug carriers to the bone marrow endothelium. The researchers attached a ligand that has a very high affinity to E-selectin to a porous silicon particle and successfully demonstrated its ability to deliver therapeutic liposomes.
These findings have the potential to further develop techniques to deliver currently available drugs specifically to the bone marrow, decreasing their side effects and improving their overall effectiveness in treating bone marrow associated disorders.
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Wiley-VCH Materials Science Journals
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() A. P. Mann et al., Adv. Mater., 2011 ; DOI: 10.1002/adma.201101541
A. P. Mann et al., Adv. Mater., 2011 ; DOI: 10.1002/adma.201101541
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








