Home > Press > "Smart” polymer capsules for dual-responsive drug delivery
 |
Abstract:
Targeted drug delivery has grown into an extensively studied research field exploring methods which allow selective or protected drug/tissue interactions. Triggered release systems based on the presence of physiological stimuli, such as pH, enzymes and redox-potential, have recently emerged for advanced therapeutic delivery applications.
"Smart” polymer capsules for dual-responsive drug delivery
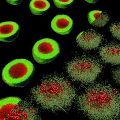
Melbourne, Australia | Posted on August 11th, 2011Professor Frank Caruso and co-workers (University of Melbourne) have demonstrated how several independent release mechanisms can be brought together and synergistically function to tune cargo release profiles. They were able to generate a novel class of polymeric nano/microcapsules with dual-responsive release mechanisms via the versatile layer-by-layer technique and click chemistry.
These capsules could release cargo specifically in pH conditions that mimic intracellular acidic compartments. Further, the synergistic effects of pH and redox-potential allowed for rapid and efficient cargo release, even for extremely low intracellular reducing agent concentrations. The simple and efficient combination of the layer-by-layer technique and click chemistry for synthesizing "big-to-small" capsules with dual stimuli-responsive cargo release mechanisms broadens the possibilities for the design of "smart" capsules for intracellular therapeutic and diagnostic applications.
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © John Wiley & Sons
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() K. Liang et al, Adv. Mater. ; DOI: 10.1002/adma.201101690
K. Liang et al, Adv. Mater. ; DOI: 10.1002/adma.201101690
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








