Home > Press > Just Add Water and... Treat Brain Cancer: Freeze-dried gene therapy system avoids virus, potential complications
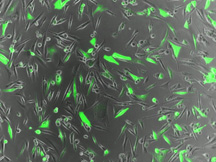 |
| Brain cancer cells produce a green fluorescent protein. DNA encoded to produce the protein was delivered to the cancer cells by new freeze-dried nanoparticles produced by Johns Hopkins biomedical engineers. Stephany Tzeng |
Abstract:
Researchers at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine have developed a technique that delivers gene therapy into human brain cancer cells using nanoparticles that can be freeze-dried and stored for up to three months prior to use.
Just Add Water and... Treat Brain Cancer: Freeze-dried gene therapy system avoids virus, potential complications
Baltimore, MD | Posted on July 8th, 2011The shelf-stable particles may obviate the need for virus-mediated gene therapy, which has been associated with safety concerns. The report appears in the August issue of Biomaterials.
"Most nonviral gene therapy methods have very low efficacy," says Jordan Green, Ph.D., an assistant professor of biomedical engineering at Johns Hopkins. "Nanoparticle-based gene therapy has the potential to be both safer and more effective than conventional chemical therapies for the treatment of cancer."
To develop the nanoparticle, Green's team started with store-bought small molecules and systematically mixed combinations together to generate chemical reactions that resulted in different polymers. They then mixed DNA that encodes a glowing protein with each different polymer to allow the DNA to bind to the polymers and form nanoparticles. Each different sample was added to human brain tumor cells and human brain tumor stem cells. After 48 hours, the team examined and counted how many cells glowed from having taken up the nanoparticles and made the glowing protein encoded by the introduced DNA.
The team rated success by counting how many cells survived and what percentage of those cells glowed.
Of the many combinations they tested, the researchers found that one particular formulation of so-called poly(beta-amino ester) nanoparticles did particularly well at getting into both glioblastoma and brain tumor stem cells. The researchers then freeze-dried these nanoparticles and stored them at different temperatures (freezer, refrigerator and room temperature) for different lengths of time (one, two and up to three months), and then retested their ability to get into cells. According to Green, after six months in storage, the effectiveness dropped by about half, but they found that up to three months of storage at room temperature there was virtually no change in effectiveness.
Furthermore, the team found that certain nanoparticles had a particular affinity for brain tumor cells over healthy brain cells.
"I could imagine particles based on this technology being used in conjunction with, and even instead of brain surgery," says Alfredo Quinones-Hinojosa, M.D., Ph.D., an associate professor of neurosurgery and oncology at Johns Hopkins. "I envision that one day, as we understand the etiology and progression of brain cancer, we will be able to use these nanoparticles even before doing surgery-how nice would that be? Imagine avoiding brain surgery altogether."
This study was funded by the Institute for NanoBioTechnology at The Johns Hopkins University, the Maryland Stem Cell Research Fund, National Institutes of Health, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation.
Authors on the paper are Stephany Tzeng, Hugo Guerrero-Cazares, Elliott Martinez, Joel Sunshine, Alfredo Quinones-Hinojosa and Jordan Green, all of Johns Hopkins.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contacts:
Mary Spiro
410-516-4802
Vanessa McMains
410-502-9410
Audrey Huang
410-614-5105
Maryalice Yakutchik
443-287-2251
Copyright © Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Institute for NanoBioTechnology
Institute for NanoBioTechnology
![]() Department of Biomedical Engineering
Department of Biomedical Engineering
![]() Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Johns Hopkins
Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Johns Hopkins
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








