Home > Press > DNAsomes' can deliver multiple drugs or genetic therapy
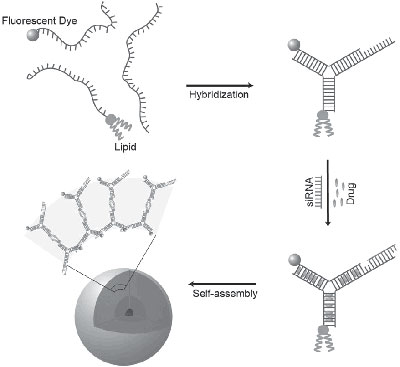 |
| DNAsomes begin with short chains of synthetic DNA designed to be complementary over part of their length so they will join into microscopic Y-shapes. A lipid molecule is attached, and fluorescent dyes can be attached for tracking. Drugs or RNA are chemically bonded to the Y-shaped unit, then many units assembled into a sphere, about the size of a virus, that can enter cells and deliver their payload. |
Abstract:
DNA isn't just for genetics anymore. Cornell researchers are using synthetic DNA to make nanoparticles, dubbed DNAsomes, that can deliver drugs and genetic therapy to the insides of cells.
DNAsomes' can deliver multiple drugs or genetic therapy
Ithaca, NY | Posted on April 22nd, 2011Dan Luo, professor of biological and environmental engineering, and colleagues report their work in the Jan. 3 issue of the journal Small.
DNAsomes, Luo said, can carry multiple drugs as well as RNA molecules designed to block the expression of genes, an improvement over other drug-delivery systems such as liposomes (tiny wrappers of the phospholipid molecules that make up cell membranes) or polymer nanoparticles. Also, some other delivery systems can be toxic to cells, the researchers said.
In its natural habitat in the nucleus of a cell, DNA consists of long chain molecules that are complementary, attaching to one another like a string of Lego blocks over their entire length to form the famous double helix. The Luo research group creates short chains of synthetic DNA designed to attach over only part of their length so they will join into shapes like crosses, Ts or Ys.
DNAsomes are assembled from Y-shaped units, each made up of three strands of DNA. A lipid molecule is attached to the tail of the Y, and drugs to be delivered are chemically bonded to the arms. When the goal is to block the expression of genes with molecules of siRNA (small interfering RNA), the synthetic DNA can be designed with a section complementary to the RNA so that the RNA will loosely attach to it. Delivering siRNA has been a particular challenge for other drug-delivery systems, the researchers noted.
In water solution, the combination of DNA, which is attracted to water molecules, and lipids, which are repelled by water, causes the Y units to self-assemble into hollow spheres from 100 to 5,000 nanometers in diameter, consisting of multiple layers of DNA, lipid and cargo.
"The beauty of this is that the body of the thing is also a body of drugs," Luo said. About the size of a virus, the DNAsome will be engulfed by the cell membrane and taken into a cell in a similar way as a virus, he explained. The DNAsome can be tagged with molecules that target a particular kind of cell, such as a cancer cell.
What happens inside the cell to release the drugs is still a "black box," Luo said, as it is with other drug-delivery systems, but tests show that the cargo is delivered. The researchers loaded DNAsomes with a fluorescent dye and introduced them into a culture of hamster ovarian cells. Microphotos showed the ovarian cells glowing under ultraviolet light. Notably, the researchers found, the cargo had been delivered both to the cytoplasm and nucleus of the cells, an important consideration for multiple drug delivery, since different drugs might have different targets in the cell. In later experiments the researchers verified the ability of DNAsomes to deliver multiple drugs as well as siRNA.
DNAsomes are named by analogy with liposomes. The suffix --some comes from a Latin word meaning "body."
The lead researcher on the study is Young Hoon Roh, who was a graduate student in the Luo group and has just received his Ph.D. David Muller, professor of applied and engineering physics, and his research group collaborated in the project. The research was supported by the U.S. Department of Agriculture and the National Science Foundation (NSF). One of the participating graduate students is supported by a Royal Thai Government Scholarship. Some of the work was performed at the Cornell Nanobiotechnology Center and the Cornell Center for Materials research, both supported by the NSF, Cornell and industrial affiliates.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Bill Steele
(607) 254-8093
Chronicle Online
312 College Ave.
Ithaca, NY 14850
607.255.4206
Blaine Friedlander
(607) 254-8093
Copyright © Cornell University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








