Home > Press > High efficiency infrared photodetectors using gold nanorods
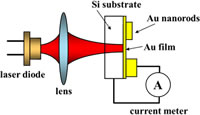 |
| Fig. 1 shows the structure and dimension of the gold nanorod Schottky diode photodetector, where 10 nm x 100 nm gold rods were used. Fig .2 shows the experimental set up and Fig. 3 the experimental results for light of 1500 nm, showing a significant increase in the photocurrent of the device with the gold nano rods. |
Abstract:
Toyohashi Tech researchers develop an innovative infrared photodetector exploiting ‘plasmon resonance' at the surface of the Au nanorods, which enhances the density of photoelectrons excited over the Schottky barrier. This technology shows potential as the basis for the development of high efficiency infra-red photodetectors for optical communications systems.
High efficiency infrared photodetectors using gold nanorods
Japan | Posted on March 22nd, 2011Devices used for the detection of light and other forms of electromagnetic energy include calorimeters, superconducting devices, and photodiodes used in optical communications systems.
Now, typical semiconductor devices include Schottky barrier photodetectors—where a PN junction is not necessary. However, for optical communications systems applications, it is necessary to improve the photo detection efficiency in the 1.3~1.5 micrometer range of wavelengths.
Here, Mitsuo Fukuda and colleagues used the localized surface plasmon (LSP) effects exhibited by gold nano-rods to improve the optical response of Schottky photodiodes. Notably, the desired resonance wavelength can be obtained by appropriate choice of the dimensions of gold nanorods. Thus combining Schottky barriers with gold nanorods holds promise as a means of producing high efficiency photodiodes.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Toyohashi University of Technology
1-1 Hibarigaoka, Tempaku
Toyohashi, Aichi Prefecture, 441-8580, JAPAN
Inquiries: International Affairs Division
E-mail:
TEL: +81-532-44-6577 or +81-532-44-6546
FAX: +81-532-44-6557
Copyright © Toyohashi Tech
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








