Home > Press > Nanomedical capsule in cancer treatment
 |
Abstract:
Nanobotmodels Company creates model of à drug delivery nanocapsule, which can be used to cancer treatment. Nanotechnology and nanorobotics development can boost and radically change modern drug delivery methods. This is our vision of cancer-treatment in the next decade.
Nanomedical capsule in cancer treatment
Ukraine | Posted on March 9th, 2010Drug delivery is a method of administering a pharmaceutical compound to achieve a therapeutic effect in humans.
Today drug delivery technologies are patent protected formulation technologies that modify drug release profile, absorption, distribution and elimination for the benefit of improving product efficacy and safety, as well as patient convenience and compliance.
Most common methods of delivery include the preferred non-invasive peroral, topical, transmucosal and inhalation routes.
Many medications such as peptide and protein, antibody, vaccine and gene based drugs, in general may not be delivered using these routes because they might be susceptible to enzymatic degradation or can not be absorbed into the systemic circulation efficiently due to molecular size and charge issues to be therapeutically effective. For this reason many protein and peptide drugs have to be delivered by injection. For example, many immunizations are based on the delivery of protein drugs and are often done by injection.
Targeted drug delivery is a method of delivering medication to a patient in a manner that increases the concentration of the medication in some parts of the body relative to others.
In traditional drug delivery systems such as oral ingestion or intravascular injection, the medication is distributed throughout the body through the systemic blood circulation. For most therapeutic agents, only a small portion of the medication reaches the organ to be affected. Targeted drug delivery seeks to concentrate the medication in the tissues of interest while reducing the relative concentration of the medication in the remaining tissues. This improves efficacy of the while reducing side effects.
The idea of using nanorobots or nanocapsule to deliver drugs and fight diseases such as cancers is not new. But there are still lots of issues to solve before nanocapsule can diagnose our diseases and treat them.
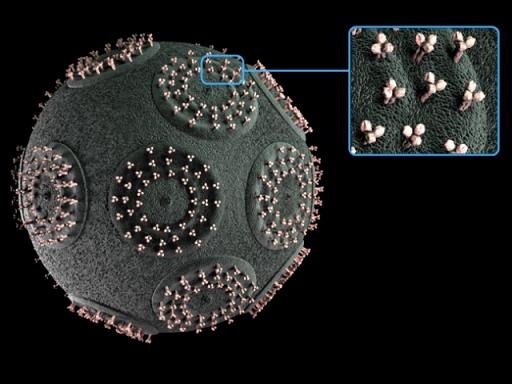
But some little steps in this direction we can do now. Such nanocapsule can be widely used in medical applications. Programmable drug delivery nanomechanical capsule is the next step in the target drug delivery technology. Size of nanocapsule is near 1 micron.
When nanocapsule injected in cancer tissues, it protein binding sites attract cancer markers on the surface of cancer cells. Proteins, acting as binding sites, change electric properties of nanocapsule injection port. Then nanocapsule CPU can activate injection mechanism to delivery agent, which cause apoptosis of the cell.
This model, made by Nanobotmodels Company, demonstrate all main parts of mechanical capsule - injection ports, binding sites, injector needle. Model made on the base of various researches on the drug delivery and nanomedicine field.
More pictures here: www.nanobotmodels.com/node/43
####
About Nanobotmodels
Our company Nanobotmodels (www.nanobotmodels.com) was founded in 2007 and it goal is develop modern art-science-technology intersections. Nanotechnology boost medicine, engeneering, biotechnology, electronics soon, so artwork and vision of the nanofuture will be very useful.
Our team consist of modern artists, modellers and nanotechnology scientists.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
common questions:
sales and image permissions:
Svidinenko Yuriy, Nanobotmodels Company CEO
Phone: +38 (096) 470 41 66
Copyright © Nanobotmodels
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








