Home > Press > Magnetic Nanoparticles Show Promise for Combating Human Cancer
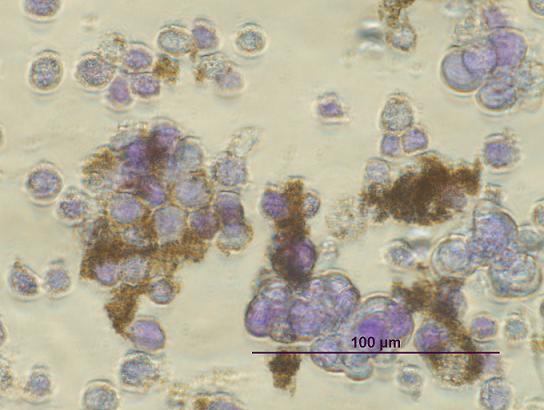 |
| Magnetic Nanoparticles Attach to Human Cancer Cells |
Abstract:
Scientists at Georgia Tech and the Ovarian Cancer Institute have further developed a potential new treatment against cancer that uses magnetic nanoparticles to attach to cancer cells, removing them from the body. The treatment, tested in mice in 2008, has now been tested using samples from human cancer patients. The results appear online in the journal Nanomedicine.
Magnetic Nanoparticles Show Promise for Combating Human Cancer
Atlanta, GA | Posted on February 2nd, 2010"We are primarily interested in developing an effective method to reduce the spread of ovarian cancer cells to other organs," said John McDonald, professor at the the School of Biology at the Georgia Institute of Technology and chief research scientist at the Ovarian Cancer Institute.
The idea came to the research team from the work of Ken Scarberry, then a Ph.D. student at Tech. Scarberry originally conceived of the idea as a means of extracting viruses and virally infected cells. At his advisor's suggestion Scarberry began looking at how the system could work with cancer cells.
He published his first paper on the subject in the Journal of the American Chemical Society in July 2008. In that paper he and McDonald showed that by giving the cancer cells of the mice a fluorescent green tag and staining the magnetic nanoparticles red, they were able to apply a magnet and move the green cancer cells to the abdominal region.
Now McDonald and Scarberry, currently a post-doc in McDonald's lab, has showed that the magnetic technique works with human cancer cells.
"Often, the lethality of cancers is not attributed to the original tumor but to the establishment of distant tumors by cancer cells that exfoliate from the primary tumor," said Scarberry. "Circulating tumor cells can implant at distant sites and give rise to secondary tumors. Our technique is designed to filter the peritoneal fluid or blood and remove these free floating cancer cells, which should increase longevity by preventing the continued metastatic spread of the cancer."
In tests, they showed that their technique worked as well with at capturing cancer cells from human patient samples as it did previously in mice. The next step is to test how well the technique can increase survivorship in live animal models. If that goes well, they will then test it with humans.
####
About Georgia Institute of Technology
The Georgia Institute of Technology is one of the nation's top research universities, distinguished by its commitment to improving the human condition through advanced science and technology.
Georgia Tech's campus occupies 400 acres in the heart of the city of Atlanta, where 20,000 undergraduate and graduate students receive a focused, technologically based education.
Accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools (SACS), the Institute offers many nationally recognized, top-ranked programs. Undergraduate and graduate degrees are offered in the Colleges of Architecture, Engineering, Sciences, Computing, Management, and the Ivan Allen College of Liberal Arts. Georgia Tech is consistently ranked in U.S. News & World Report's top ten public universities in the United States.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Terraso
Communications and Marketing
404-385-2966
Copyright © Georgia Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








