Home > Press > Researchers Develop New Tool for Gene Delivery
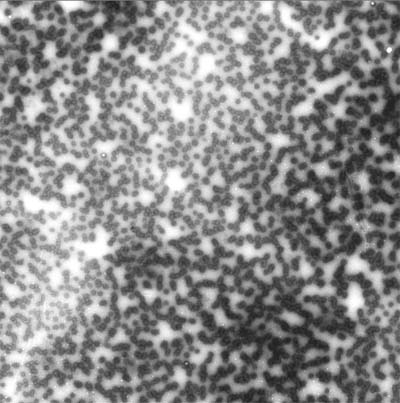 |
| Electron Micrograph of PEG-POD DNA complexes indicates that each nanoparticle is approximately 136 nm in size. Credit: courtesy of Tufts University School of Medicine. |
Abstract:
Researchers at Tufts University School of Medicine and the Sackler School of Graduate Biomedical Sciences at Tufts have developed a new tool for gene therapy that significantly increases gene delivery to cells in the retina compared to other carriers and DNA alone, according to a study published in the January issue of The Journal of Gene Medicine.
Researchers Develop New Tool for Gene Delivery
Boston, MA | Posted on January 27th, 2010The tool, a peptide called PEG-POD, provides a vehicle for therapeutic genes and may help researchers develop therapies for degenerative eye disorders such as retinitis pigmentosa and age-related macular degeneration.
"For the first time, we have demonstrated an efficient way to transfer DNA into cells without using a virus, currently the most common means of DNA delivery. Many non-viral vectors for gene therapy have been developed but few, if any, work in post-mitotic tissues such as the retina and brain. Identifying effective carriers like PEG-POD brings us closer to gene therapy to protect the retinal cells from degeneration," said senior author Rajendra Kumar-Singh, PhD, associate professor of ophthalmology and adjunct associate professor of neuroscience at Tufts University School of Medicine (TUSM) and member of the genetics; neuroscience; and cell, molecular, and developmental biology program faculties at the Sackler School of Graduate Biomedical Sciences at Tufts.
Safe and effective delivery of therapeutic genes has been a major obstacle in gene therapy research. Deactivated viruses have frequently been used, but concerns about the safety of this method have left scientists seeking new ways to get therapeutic genes into cells.
"We think the level of gene expression seen with PEG-POD may be enough to protect the retina from degeneration, slowing the progression of eye disorders and we have preliminary evidence that this is indeed the case," said co-author Siobhan Cashman, PhD, research assistant professor in the department of ophthalmology at TUSM and member of Kumar-Singh's lab.
"What makes PEG-POD especially promising is that it will likely have applications beyond the retina. Because PEG-POD protects DNA from damage in the bloodstream, it may pave the way for gene therapy treatments that can be administered through an IV and directed to many other parts of the body," said Kumar-Singh.
Kumar-Singh and colleagues used an in vivo model to compare the effectiveness of PEG-POD with two other carriers (PEG-TAT and PEG-CK30) and a control (injections of DNA alone).
"Gene expression in specimens injected with PEG-POD was 215 times greater than the control. While all three carriers delivered DNA to the retinal cells, PEG-POD was by far the most effective," said first author Sarah Parker Read, an MD/PhD candidate at TUSM and Sackler and member of Kumar-Singh's lab.
Age-related macular degeneration, which results in a loss of sharp, central vision, is the number one cause of vision loss in Americans age 60 and older. Retinitis pigmentosa, an inherited condition resulting in retinal damage, affects approximately 1 in 4,000 individuals in the United States.
This study was supported by grants from the National Eye Institute of the National Institutes of Health, the Foundation for Fighting Blindness, The Ellison Foundation, The Virginia B. Smith Trust, the Lions Eye Foundation, and Research to Prevent Blindness. Sarah Parker Read is part of the Sackler/TUSM Medical Scientist Training Program, which is funded by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, part of the National Institutes of Health.
Read SP, Cashman SM, Kumar-Singh R. The Journal of Gene Medicine. 2010 (January). 12(1): 86-96. "A poly(ethylene) glycolylated peptide for ocular delivery compacts DNA into nanoparticles for gene delivery to post-mitotic tissues in vivo." Doi: 10.1002/jgm.1415
####
About Tufts University
Tufts University School of Medicine and the Sackler School of Graduate Biomedical Sciences at Tufts University are international leaders in innovative medical education and advanced research. The School of Medicine and the Sackler School are renowned for excellence in education in general medicine, biomedical sciences, special combined degree programs in business, health management, public health, bioengineering and international relations, as well as basic and clinical research at the cellular and molecular level.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Siobhan Gallagher
617-636-6586
Copyright © Tufts University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








