Home > Press > Research promises tears of joy for diabetics
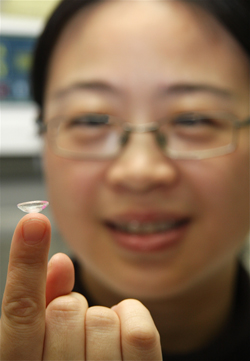 |
| The work of Chemical & Biochemical assistant professor Jin Zhang, and the use of extremely small nanoparticles in contact lenses, may soon change the way diabetics monitor their glucose levels. |
Abstract:
A simple pair of contact lenses may soon alleviate the need for diabetics to regularly draw blood in order to test their glucose levels.
Research promises tears of joy for diabetics
Ontario, Canada | Posted on January 15th, 2010Through the use of nanotechnology, University of Western Ontario Chemical and Biochemical Assistant professor Jin Zhang is using extremely small particles embedded in the hydrogel contact lenses to monitor and report on changing sugar levels in the body.
These engineered nanoparticles react with glucose molecules found in tears - similar to those found in blood - causing a chemical reaction. When there is a variation in a person's sugar level, the contact lenses respond by changing their color.
"I know how people can suffer from having to continually monitoring their blood. It can be very uncomfortable," she says. "This non-invasive method is now an alternative choice to help manage their treatment. People realize how significant it can be, so it's very easy to get excited."
Zhang is cross-appointed with London's Ivey Eye Institute, affiliated with the university, and is working with clinical doctors on her research. She recently received $216,342 from the Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI) to further develop her research.
But while she is excited about the progress of her research and the attention it is receiving, Zhang is well aware there is still plenty of work to be done. The project has been ongoing for more than two years, working with her multifunctional nanocomposites group in Engineering.
"It has worked in the lab," she says. "However, there are still several challenges to get through, such as industry partners."
Also, the nanoparticles are only able to detect specific changes in glucose levels and Zhang would like to see her research allow for the detection of even more subtle changes. Zhang is also researching ways to make the sensors be able to detect other components in tears, such as calcium, which could be used to test for osteoporosis.
"The goal is to make this simple and safe," says Zhang, "We are getting closer and closer and with the CFI support, it will definitely speed up the research. We have a great environment here at Western to make this project move forward."
####
About University of Western Ontario
The University of Western Ontario - Western provides the best student experience among Canada's leading research-intensive universities.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Publisher:
Helen Connell
Editor:
David Dauphinee
Reporter/Photographer:
Paul Mayne
Reporter/Photographer:
Heather Travis
Copyright © University of Western Ontario
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








