Home > Press > JQI Researchers Create ‘Synthetic Magnetic Fields’ for Neutral Atoms
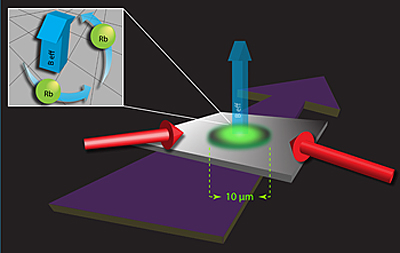 |
| A pair of laser beams (red arrows) impinges upon an ultracold gas cloud of rubidum atoms (green oval) to create synthetic magnetic fields (labeled Beff). (Inset) The beams, combined with an external magnetic field (not shown) cause the atoms to "feel" a rotational force; the swirling atoms create vortices in the gas. Credit: JQI |
Abstract:
Achieving an important new capability in ultracold atomic gases, researchers at the Joint Quantum Institute, a collaboration of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Maryland, have created "synthetic" magnetic fields for ultracold gas atoms, in effect "tricking" neutral atoms into acting as if they are electrically charged particles subjected to a real magnetic field.
JQI Researchers Create ‘Synthetic Magnetic Fields’ for Neutral Atoms
Gaithersburg, MD | Posted on January 11th, 2010The demonstration, described in the latest issue of the journal Nature, not only paves the way for exploring the complex natural phenomena involving charged particles in magnetic fields, but may also contribute to an exotic new form of quantum computing.
As researchers have become increasingly proficient at creating and manipulating gaseous collections of atoms near absolute zero, these ultracold gases have become ideal laboratories for studying the complex behavior of material systems. Unlike usual crystalline materials, they are free of obfuscating properties, such as impurity atoms, that exist in normal solids and liquids. However, studying the effects of magnetic fields is problematic because the gases are made of neutral atoms and so do not respond to magnetic fields in the same way as charged particles do. So how would you simulate, for example, such important exotic phenomena as the quantum Hall effect, in which electrons can "divide" into quasiparticles carrying only a fraction of the electron's electric charge?
The answer Ian Spielman and his colleagues came up with is a clever physical trick to make the neutral atoms behave in a way that is mathematically identical to how charged particles move in a magnetic field. A pair of laser beams illuminates an ultracold gas of rubidium atoms already in a collective state known as a Bose-Einstein condensate. The laser light ties the atoms' internal energy to their external (kinetic) energy, modifying the relationship between their energy and momentum. Simultaneously, the researchers expose the atoms to a real magnetic field that varies along a single direction, so that the alteration also varies along that direction. In a strange inversion, the laser-illuminated neutral atoms react to the varying magnetic field in a way that is mathematically equivalent to the way a charged particle responds to a uniform magnetic field. The neutral atoms experience a force in a direction perpendicular to both their direction of motion and the direction of the magnetic field gradient in the trap. By fooling the atoms in this fashion, the researchers created vortices in which the atoms swirl in whirlpool-like motions in the gas clouds. The vortices are the "smoking gun," Spielman says, for the presence of synthetic magnetic fields.
Previously, other researchers had physically spun gases of ultracold atoms to simulate the effects of magnetic fields, but rotating gases are unstable and tend to lose atoms at the highest rotation rates. In their next step, the JQI researchers plan to partition a nearly spherical system of 20,000 rubidium atoms into a stack of about 100 two-dimensional "pancakes" and increase their currently observed 12 vortices to about 200 per-pancake. At a one-vortex-per-atom ratio, they could observe the quantum Hall effect and control it in unprecedented ways. In turn, they hope to coax atoms to behave like a class of quasiparticles known as "non-abelian anyons," a required component of "topological quantum computing," in which anyons dancing in the gas would perform logical operations based on the laws of quantum mechanics.
* Y.J. Lin, R.L. Compton, K. Jimenez-Garcia, J.V. Porto and I.B. Spielman. Synthetic magnetic fields for ultracold neutral atoms. Nature, Dec. 3, 2009.
####
About NIST
From automated teller machines and atomic clocks to mammograms and semiconductors, innumerable products and services rely in some way on technology, measurement, and standards provided by the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
Founded in 1901, NIST is a non-regulatory federal agency within the U.S. Department of Commerce. NIST's mission is to promote U.S. innovation and industrial competitiveness by advancing measurement science, standards, and technology in ways that enhance economic security and improve our quality of life.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ben Stein
(301) 975-3097
Copyright © NIST
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








