Home > Press > NETL Researchers Develop Promising New Photocatalyst for CO2 Reuse
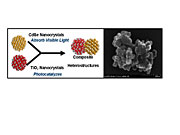 |
| (Left panel) Schematic diagram of the new photocatalytic technology for converting CO2 into fuels. (Right panel) SEM image of a heterostructured CdSe/Pt/TiO2 photocatalyst synthesized and tested by the NETL team (scale bar 100 nm). |
Abstract:
Researchers at the National Energy Technology Laboratory have developed a new, heterostructured photocatalyst capable of using the low-energy, visible-light portion of the electromagnetic spectrum for converting CO2 and H2O into methane, methanol, and other value-added chemicals.
NETL Researchers Develop Promising New Photocatalyst for CO2 Reuse
Pittsburgh, PA | Posted on December 22nd, 2009In this system, CdSe nanocrystals absorb visible light photons, creating excited electrons which are injected into TiO2 to reduce CO2. The photoactivity of this system can be systematically tuned to utilize different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum just by changing the size of the CdSe nanocrystal photosensitizer. This catalyst is believed to be the first developed that is capable of using the low-energy, visible-light portion of the electromagnetic spectrum for this process, and it represents a significant advance in the development of new technologies for CO2 capture and reuse. A manuscript detailing this new photocatalyst has been published in the Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, and a provisional patent has also been filed on the technology.
####
About National Energy Technology Laboratory
The National Energy Technology Laboratory (NETL), part of DOE’s national laboratory system, is owned and operated by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE). NETL supports DOE’s mission to advance the national, economic, and energy security of the United States.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Customer Service Line:
(800) 553-7681
Copyright © National Energy Technology Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








