Home > Press > Quantum mechanics on the cheap
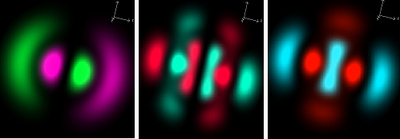 |
| Electron distributions around atoms (Images courtesy of IBM) |
Abstract:
NPL, together with IBM and the University of Edinburgh, have developed a new technique that dramatically improves the accuracy and efficiency of computer models of materials. By applying aspects of quantum mechanics in new ways, highly accurate simulations of materials may be achieved quicker and more efficiently than is currently possible with standard methods.
Quantum mechanics on the cheap
UK | Posted on October 8th, 2009Quantum mechanics is all about understanding how things behave at the atomic scale. Many computer simulations of materials make simple assumptions about how a material behaves at the atomic scale which do not necessarily reflect reality and compromise predictive power.
Incorporating improved physical descriptions of quantum phenomena is a major challenge and advances in this area is great news for developers of next-generation materials for use in biotechnology, nanotechnology and other areas of cutting-edge science where more rational design input from computer models is needed.
For example, computer models can simulate conditions that are not easy to recreate in the laboratory, or to reveal the properties of materials not yet synthesised thereby reducing costly 'real world' development time. But they are only as good as the mathematical assumptions upon which they are based. Most current computer models, for example, cannot account for the fact that electrons move around, and are influenced by their surroundings. This complex response of electrons at the atomic scale can influence exploitable material properties and phenomena relevant to microelectronics and biological binding events.
The new approach, reported in Physical Review B and demonstrated for the case of solid Xenon, addresses the complexities of electronic responses in a unified framework leading to the prospect of applications to much larger systems.
For more technical information about this research, please see the paper, which was recently published in Physical Review B.
####
About National Physical Laboratory
As the UK’s National Measurement Institute, NPL’s mission is:
* Excellence in science
* Increased exploitation of that science to boost UK competitiveness and quality of life
* Integrity and independence as a national asset
* Enhanced international standing
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Prof Jason Crain
Team Research & International
Phone +44 20 8943 6107
Copyright © National Physical Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Download Physical Review B. paper
Download Physical Review B. paper
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








