Home > Press > Carbon nanotubes could make efficient solar cells
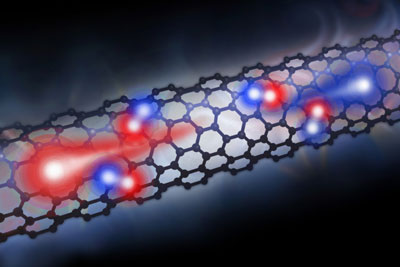 |
| In a carbon nanotube-based photodiode, electrons (blue) and holes (red) - the positively charged areas where electrons used to be before becoming excited - release their excess energy to efficiently create more electron-hole pairs when light is shined on the device. |
Abstract:
Using a carbon nanotube instead of traditional silicon, Cornell researchers have created the basic elements of a solar cell that hopefully will lead to much more efficient ways of converting light to electricity than now used in calculators and on rooftops.
Carbon nanotubes could make efficient solar cells
Ithica, NY | Posted on September 10th, 2009The researchers fabricated, tested and measured a simple solar cell called a photodiode, formed from an individual carbon nanotube. Reported online Sept. 11 in the journal Science, the researchers -- led by Paul McEuen, the Goldwin Smith Professor of Physics, and Jiwoong Park, assistant professor of chemistry and chemical biology -- describe how their device converts light to electricity in an extremely efficient process that multiplies the amount of electrical current that flows. This process could prove important for next-generation high efficiency solar cells, the researchers say.
"We are not only looking at a new material, but we actually put it into an application -- a true solar cell device," said first author Nathan Gabor, a graduate student in McEuen's lab.
The researchers used a single-walled carbon nanotube, which is essentially a rolled-up sheet of graphene, to create their solar cell. About the size of a DNA molecule, the nanotube was wired between two electrical contacts and close to two electrical gates, one negatively and one positively charged. Their work was inspired in part by previous research in which scientists created a diode, which is a simple transistor that allows current to flow in only one direction, using a single-walled nanotube. The Cornell team wanted to see what would happen if they built something similar, but this time shined light on it.
Shining lasers of different colors onto different areas of the nanotube, they found that higher levels of photon energy had a multiplying effect on how much electrical current was produced.
Further study revealed that the narrow, cylindrical structure of the carbon nanotube caused the electrons to be neatly squeezed through one by one. The electrons moving through the nanotube became excited and created new electrons that continued to flow. The nanotube, they discovered, may be a nearly ideal photovoltaic cell because it allowed electrons to create more electrons by utilizing the spare energy from the light.
This is unlike today's solar cells, in which extra energy is lost in the form of heat, and the cells require constant external cooling.
Though they have made a device, scaling it up to be inexpensive and reliable would be a serious challenge for engineers, Gabor said.
"What we've observed is that the physics is there," he said.
The research was supported by Cornell's Center for Nanoscale Systems and the Cornell NanoScale Science and Technology Facility, both National Science Foundation facilities, as well as the Microelectronics Advanced Research Corporation Focused Research Center on Materials, Structures and Devices. Research collaborators also included Zhaohui Zhong, of the University of Michigan, and Ken Bosnick, of the National Institute for Nanotechnology at University of Alberta.
####
About Cornell University
Once called "the first American university" by educational historian Frederick Rudolph, Cornell University represents a distinctive mix of eminent scholarship and democratic ideals. Adding practical subjects to the classics and admitting qualified students regardless of nationality, race, social circumstance, gender, or religion was quite a departure when Cornell was founded in 1865.
Today's Cornell reflects this heritage of egalitarian excellence. It is home to the nation's first colleges devoted to hotel administration, industrial and labor relations, and veterinary medicine. Both a private university and the land-grant institution of New York State, Cornell University is the most educationally diverse member of the Ivy League.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact:
Blaine Friedlander
(607) 254-8093
Cornell Chronicle:
Anne Ju
(607) 255-9735
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








