Home > Press > Dolomite Microfluidic Glass Chip Separates Biological Molecules
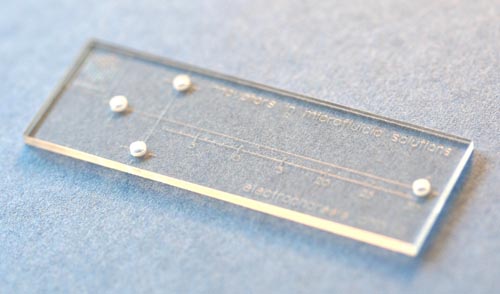 |
| Mitos electrophoresis chip |
Abstract:
The Mitos capillary electrophoresis chip A separates species on their size to charge ratio
Dolomite Microfluidic Glass Chip Separates Biological Molecules
Royston, UK | Posted on July 15th, 2009Dolomite, a world leader in microfluidic design and manufacture, has introduced the glass Mitos Capillary Electrophoresis Chip A to separate small quantities of biological molecules by capillary electrophoresis. Measuring only 15 x 45 x 2 mm, this electrophoresis chip combines a cross channel design with a 20 µm channel depth and a 30 mm long channel for accurate analysis of the separation.
With excellent chemical compatibility, the Mitos Capillary Electrophoresis Chip A separates species in the interior of the microchannel based on their size to charge ratio. The high surface to volume ratio of the microchannels enables the application of high voltages without overheating the samples. Furthermore, an extremely smooth channel surface, in combination with a wide pressure and temperature range make it ideal for a broad range of applications.
Dolomite also allows users to custom design chips with straight channels up to 150 mm in length, for improved detection sensitivity. Furthermore, the electrophoresis chip can be fabricated with a channel depth varying from 250 nm to 300 µm, allowing accurate analysis of different sample volumes. The thickness of the top and base layers can range from 150 µm to 5 mm, and the
entire chip can be fabricated from quartz, if required. With excellent optical transmission and high visibility, this chip allows excellent access for microscope-based inspection systems.
For further information on the Mitos Capillary Electrophoresis Chip A as well as the full range of microfluidic capabilities available from Dolomite including pumps, interconnects, chips and valves, please visit www.dolomite-microfluidics.com.
####
About Dolomite
Dolomite is a global leader in the design and manufacture of microfluidics devices. With offices in the UK, US and Japan and distributors throughout the rest of the world, its clients range from universities developing leading-edge analytical equipment, to manufacturers of chemical, life sciences and clinical diagnostics systems.
Excellent microfabrication facilities that include cleanrooms, precision glass processing facilities and applications laboratories were established with Ł2m in funding from the UK Department of Trade and Industry's Micro and Nano Technology (MNT) Manufacturing Initiative. Dolomite’s expertise includes top quality engineering and scientific staff with strong backgrounds across the broad range of disciplines required for success in bringing microfluidics applications to the market, including chemistry, biotechnology, control system development, electronics, physics and instrument design and supply.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Product enquiries
Dolomite
Mike Hawes
+44 1763 242491
Tim Landucci
+44 1763 242491
Media enquiries
Alto Marketing Limited
Clare Russell
+44 (0)1489 557672
Copyright © Dolomite
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Products
![]() Spectradyne Partners with Particle Technology Labs for Measurement Services December 6th, 2018
Spectradyne Partners with Particle Technology Labs for Measurement Services December 6th, 2018
![]() Mode-Changing MEMS Accelerometer from STMicroelectronics Combines High Measurement Resolution and Ultra-Low Power for Industrial Applications November 7th, 2018
Mode-Changing MEMS Accelerometer from STMicroelectronics Combines High Measurement Resolution and Ultra-Low Power for Industrial Applications November 7th, 2018
![]() Fat-Repellent Nanolayers Can Make Oven Cleaning Easier October 17th, 2018
Fat-Repellent Nanolayers Can Make Oven Cleaning Easier October 17th, 2018
![]() Aculon, Inc. Enters into Strategic Partnership Agreement with Henkel Corporation to Supply Key Mobile Device Manufacturers with NanoProof® PCB Waterproof Technology October 17th, 2018
Aculon, Inc. Enters into Strategic Partnership Agreement with Henkel Corporation to Supply Key Mobile Device Manufacturers with NanoProof® PCB Waterproof Technology October 17th, 2018
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








