Home > Press > Long-sought way to make “nano-raspberries” may fight foggy windows and eyeglasses
 |
| A new method for making raspberry-shaped nanoparticles could prevent windshields and eyeglasses from fogging. Credit: The American Chemical Society |
Abstract:
The Journal of Physical Chemistry C
Long-sought way to make “nano-raspberries” may fight foggy windows and eyeglasses
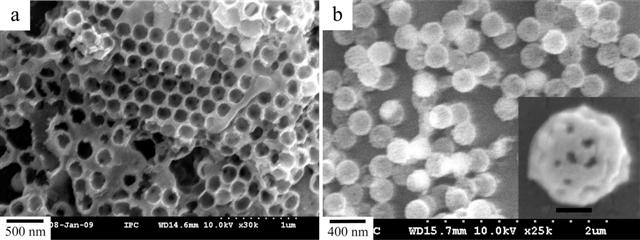
Washington, DC | Posted on May 20th, 2009In an advance toward preventing car windshields and eyeglasses from fogging up, researchers in China are reporting development of a new way to make raspberry-shaped nanoparticles that can give glass a permanent antifogging coating. Their study is scheduled for the June 11 edition of ACS' The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, a weekly publication.
Junhui He and colleagues note that researchers have been working on anti-fog technology for years. Fogged-up windows are a safety hazard and a nuisance that affect millions of people. Existing technology, including sprays that must be reapplied to stay effective, has many drawbacks. Researchers knew that raspberry-shaped nanoparticles could be the ideal solution by disrupting the process in which water droplets fog glass. Until now, however, there has been no commercially feasible way to make these particles.
The scientists describe an efficient one-step method for making nano-raspberries. In laboratory studies, the researchers coated glass slides with the particles, cooled the slide, and then exposed it to steam. Unlike ordinary glass, it remained crystal clear, opening the door to possible commercial applications, the researchers say.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Junhui He, Ph.D.
Functional Nanomaterials Laboratory
Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Beijing, China
Phone: 86-10-82543535
Fax: 86-10-82543535
Copyright © American Chemical Society (ACS)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








