Home > Press > Synthetic Capsules Made of Natural Building Blocks
 |
Abstract:
Block copolymer vesicles from protein and sugar components
Synthetic Capsules Made of Natural Building Blocks
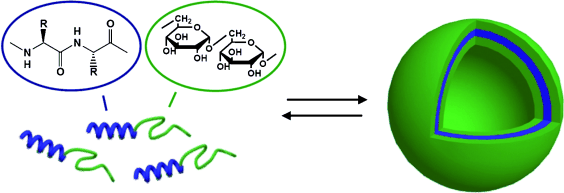
Bordeaux, France | Posted on March 23rd, 2009The basis of all life forms are vesicles: membrane-enclosed, liquid-filled "bubbles" made of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. Cells, which are separated from the surrounding medium by their cell membrane, are really just big vesicles. Small vesicles play a critical role in the intracellular transport of biomolecules. Synthetic vesicles, such as liposomes and polymersomes, made of lipids and polymers respectively, are used to transport active ingredients in products such as cosmetic or pharmaceutical formulations. They also have potential as microreactors intended to mimic the behavior of living cells. This would be more successful if the vesicles were made of natural components. As reported in the journal Angewandte Chemie, researchers working with Sébastien Lecommandoux and Christophe Schatz at the University of Bordeaux (France) have now attached together blocks of sugar molecule chains (polysaccharides) and protein chains (polypeptides) in a linear fashion. In water, these block copolymers spontaneously form vesicles.
The researchers used dextran, a polymer made of glucose building blocks, and poly(benzyl L-glutamate) (PBLG), a biocompatible polypeptide. By using a series of reactions referred to as "click" chemistry, they attached these molecules to each other blockwise. The advantages of this method are the mild reaction conditions, the nearly quantitative yield, and the fact that other functional side groups on the reactants do not interfere with the reaction.
In this way, the scientists produced block copolymers that combine a polypeptide (protein-like) block and a sugar block. The hydrophobic (water-repellant) polypeptide adopts a helical conformation and in aqueous environments prefers to be side-to-side with those like itself. This results in membrane-like layers that close in on themselves to form spherical vesicles. On both sides of the synthetic membrane, the hydrophilic (water-friendly) dextran chains coil up into a stabilizing "corona". Electron microscope images reveal membranes that are about 21 nm thick surrounding vesicles of a very uniform size (about 45 nm radius).
The researchers would like to use their simple, versatile synthetic strategy to make other synthetic glycopeptides that could be used as model compounds for the exploration of cellular sugar structures (glycomics). The vesicles could also form the basis for a new generation of drug and gene transporters, because their sugar corona binds well to glycoproteins on the surfaces of living cells. The vesicles are also similar to the hulls of viruses and are a first step toward mimicking virus morphology.
Author: Sébastien Lecommandoux, Université de Bordeaux, Pessac (France), recherche.enscpb.fr/lcpo/fr/fichier%20html/perso_lecommandoux-fr.htm
Title: Polysaccharide-block-polypeptide Copolymer Vesicles: Towards Synthetic Viral Capsids
Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2009, 48, No. 14, 2572-2575, doi: 10.1002/anie.200805895
####
Contacts:
Editorial office:
Amy Molnar (US)
Jennifer Beal (UK)
Alina Boey (Asia)
Copyright © Angewandte Chemie
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








