Home > Press > Gold particles deliver more than just glitter: Nanoparticles could carry drugs to treat cancer, other diseases
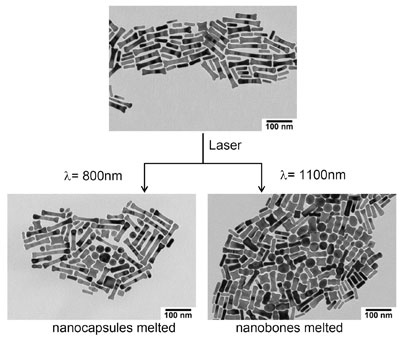 |
| The top image shows a mixture of gold nanoparticles. The longer particles are called nanobones, and the smaller are nanocapsules. Bottom left: After the nanoparticles are hit with 800 nanometer wavelength infrared light, the nanocapsules melt and release their payload. Nanobones remain intact. Right: After the nanoparticles are hit with 1100 nanometer wavelength infrared light, the nanobones melt and release their payload. Nanocapsules remain intact. Image / Andy Wijaya |
Abstract:
Using tiny gold particles and infrared light, MIT researchers have developed a drug-delivery system that allows multiple drugs to be released in a controlled fashion.
Such a system could one day be used to provide more control when battling diseases commonly treated with more than one drug, according to the researchers.
Gold particles deliver more than just glitter: Nanoparticles could carry drugs to treat cancer, other diseases
Cambridge, MA | Posted on December 30th, 2008"With a lot of diseases, especially cancer and AIDS, you get a synergistic effect with more than one drug," said Kimberly Hamad-Schifferli, assistant professor of biological and mechanical engineering and senior author of a paper on the work that recently appeared in the journal ACS Nano.
Delivery devices already exist that can release two drugs, but the timing of the release must be built into the device -- it cannot be controlled from outside the body. The new system is controlled externally and theoretically could deliver up to three or four drugs.
The new technique takes advantage of the fact that when gold nanoparticles are exposed to infrared light, they melt and release drug payloads attached to their surfaces.
Nanoparticles of different shapes respond to different infrared wavelengths, so "just by controlling the infrared wavelength, we can choose the release time" for each drug, said Andy Wijaya, graduate student in chemical engineering and lead author of the paper.
The team built two different shapes of nanoparticles, which they call "nanobones" and "nanocapsules." Nanobones melt at light wavelengths of 1,100 nanometers, and nanocapsules at 800 nanometers.
In the ACS Nano study, the researchers tested the particles with a payload of DNA. Each nanoparticle can carry hundreds of strands of DNA, and could also be engineered to transport other types of drugs.
In theory, up to four different-shaped particles could be developed, each releasing its payload at different wavelengths.
Other authors of the paper are Stefan Schaffer and Ivan Pallares, who were National Science Foundation REU (Research Experiences for Undergraduates) summer students through the MIT Department of Biological Engineering in 2008.
####
About MIT
The mission of MIT is to advance knowledge and educate students in science, technology, and other areas of scholarship that will best serve the nation and the world in the 21st century.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jen Hirsch
MIT News Office
Phone: 617-253-2700
Copyright © MIT
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








