Home > Press > Nanotomography: Crystal clear
 |
Abstract:
X-rays from a synchrotron can produce incredible high-resolution three-dimensional images of nanoscale crystal structures
Researchers have combined medical imaging equipment with radiation from a particle accelerator to produce a powerful new method for three-dimensional (3D) imaging. The technique, developed by YU Shuhong, TIAN Yangchao and co-workers at the University of Science and Technology of China in Hefei,CAS, has already produced remarkable 3D renderings of a copper sulphide crystal, and could find many applications in materials development and the life sciences.
Nanotomography: Crystal clear
China | Posted on August 29th, 2008 Electron microscopes can provide detailed two-dimensional information on functional nanostructures, but are limited in applications involving complex 3D shapes. On the other hand, X-rays can penetrate to great depths and are used in medical computed-tomography scans to take images in slices that are then compiled to render a 3D image.
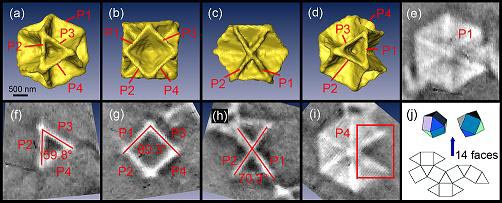
Yu, Tian and co-workers used the beamline from the National Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory in Hefei to provide a very powerful X-ray flux. The beam was carefully manipulated to make 3D images of a recently discovered type of copper sulphide crystal.
The images show that the crystal is made up of four hexagonal plates about 200 nanometres thick (pictured). Together they form a cuboctahedron - a polyhedron with six square and eight triangular faces.
The image details indicate that the X-ray technique is useful to image nanomaterials with complex structures. (adapted from Nature China)
####
About Chinese Academy of Sciences
CAS strives to build itself into a scientific research base at advanced international level, a base for fostering and bringing up advanced S&T talents, and a base for promoting the development of China's high and new technology industries. By 2010, CAS will have about 80 national institutes noted for their powerful capacities in S&T innovation and sustainable development or with distinctive features; thirty of them will become internationally acknowledged, high-level research institutions, and three to five will be world class.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Beijing China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86 10 68597289
Fax: 86 10 68512458
Chief-Editor's Information:
Guo Haiyan
Editor
Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences
CAS Institute of Policy & Management
P.O.Box 8712, Beijing 100080, China.
Copyright © Chinese Academy of Sciences
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








