Home > Press > MIT researchers tug at molecules with optical tweezers
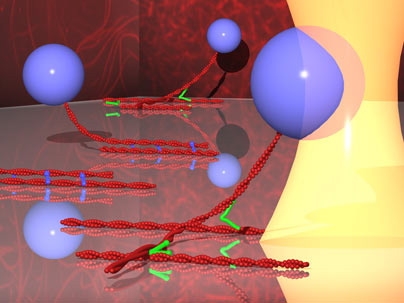 |
| The strength of actin binding protein interactions cross-linking a surface bound and bead tethered actin filament are probed using force from an optical trap. Filamin in green which forms networks of actin filaments shown as a confocal image on the right and alpha-actinin in blue which bundles actin filaments, shown as an image on the left, were probed using this assay configuration. Image courtesy / Hyungsuk Lee, Jorge M. Ferrer, and Matthew J. Lang |
Abstract:
Using a light touch to measure protein bonds
MIT researchers tug at molecules with optical tweezers
Cambridge, MA | Posted on July 2nd, 2008MIT researchers have developed a novel technique to measure the strength of the bonds between two protein molecules important in cell machinery: Gently tugging them apart with light beams.
"It's really giving us a molecular-level picture of what's going on," said Matthew Lang, an assistant professor of biological and mechanical engineering and senior author of a paper on the work appearing in the June 30 advanced online issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science.
Last fall, Lang and others demonstrated that light beams could be used to pick up and move individual cells around the surface of a microchip.
Now they have applied the optical tweezers to measuring protein microarchitectures, allowing them to study the forces that give cells their structure and the ability to move.
The researchers focused on proteins that bind to actin filaments, an important component of the cytoskeleton. Depending on the arrangement and interaction of actin filaments, they can provide structural support, help the cell crawl across a surface or sustain a load (in muscle cells).
"We're trying to understand how nature engineered these molecular linkages to use in different ways," said Lang.
Actin filaments are most commonly found either bonded or crosslinked by a much smaller actin binding protein.
The researchers studied the interactions between the proteins by pinning one actin filament to a surface and controlling the motion of the second one with a beam of light. As the researchers tug on a bead attached to the second filament, the bond mediated by the actin-binding protein eventually breaks.
With this technique, the researchers can get a precise measurement of the force holding the proteins together, which is on the order of piconewtons (10^-12 newtons).
The same technique could be used to investigate many of the other hundreds of protein interactions that occur in the cytoskeleton, said Lang.
Lead author of the paper is Jorge Ferrer, a recent PhD recipient in biological engineering. Other MIT authors of the paper are Hyungsuk Lee and Benjamin Pelz, graduate students in mechanical engineering; and Roger Kamm, the Germeshausen Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Biological Engineering.
Jiong Chen of Stony Brook University and Fumihiko Nakamura of Harvard Medical School are also authors of the paper.
The research was funded by the Nicholas Hobson Wheeles Jr. Fellowship, the W.M. Keck Foundation, and the Westaway Research Fund.
####
About MIT
The mission of MIT is to advance knowledge and educate students in science, technology, and other areas of scholarship that will best serve the nation and the world in the 21st century.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Teresa Herbert
MIT News Office
Phone: 617-258-5403
E-mail:
Copyright © MIT
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








