Home > Press > Nano-tech process produces plastics that are 10 times more stretchable
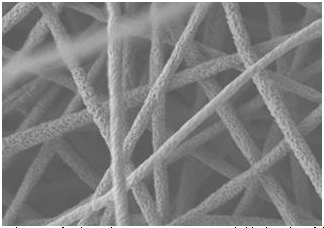 |
| Scientists report development of a plastic that is 10 times more stretchable than that of the original material. Above is a micrograph of the electrospun nano-sized fibers. Courtesy of the American Chemical Society |
Abstract:
Move over, Rumplestiltskin. Researchers in China report the first successful "electrospinning" of a type of plastic widely used in automobiles and electronics. The high-tech process, which uses an electric charge to turn polymers into thin fibers in the presence of electricity, produced plastic mats that can stretch 10 times more without breaking than the original material and could lead to new uses for the plastic, they say. Their study is scheduled for the June 10 issue of ACS' Macromolecules, a bi-weekly journal.
Nano-tech process produces plastics that are 10 times more stretchable
Beijing, Peoples Republic of China | Posted on May 28th, 2008In the new study, Zhao-Xia Guo and colleagues point out that the original plastic, called polyoxymethylene (POM), is an engineering staple known for its metal-like hardness, light weight, and resistance to chemicals. However, the material is relatively brittle, limiting its applications. Although many different types of plastics have been electrospun into fibers with extended uses and properties, researchers have been unable to spin POM into fibers until now, the researchers say.
They report that POM could be turned into nano-sized fibers — thousands of times thinner than the width of a single hair — after first dissolving it in a solution called HFIP and then undergoing electrospinning. The process resulted in POM mats with improved stretchability, or ductility, high porosity, and high surface area. Such features could extend the plastic's uses to a wide range of industrial, electronic and medical applications, the researchers say. — MTS
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Zhao-Xia Guo, Ph.D.
Tsinghua University
Beijing, Peoples Republic of China
Copyright © American Chemical Society (ACS)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








