Home > Press > Sheet of Carbon Atoms Acts like a Billiard Table, Physicists Find
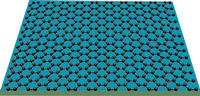 |
| Image shows graphene, which can act as an atomic-scale billiard table, with electric charges acting as billiard balls. Image credit: Lau lab, UCR. |
Abstract:
UC Riverside research shows graphene, a thin sheet of carbon atoms, has good potential to supplement or replace silicon as an electronic material
Sheet of Carbon Atoms Acts like a Billiard Table, Physicists Find
RIVERSIDE, CA | Posted on September 14th, 2007A game of billiards may never get smaller than this.
Physicists at UC Riverside have demonstrated that graphene - a one-atom thick sheet of carbon atoms arranged in hexagonal rings - can act as an atomic-scale billiard table, with electric charges acting as billiard balls.
The finding underscores graphene's potential for serving as an excellent electronic material, such as silicon, that can be used to develop new kinds of transistors based on quantum physics. Because they encounter no obstacles, the electrons in graphene roam freely across the sheet of carbon, conducting electric charge with extremely low resistance.
Study results appear in today's issue of Science.
The research team, led by Chun Ning (Jeanie) Lau, found that the electrons in graphene are reflected back by the only obstacle they meet: graphene's boundaries.
"These electrons meet no other obstacles and behave like quantum billiard balls," said Lau, an assistant professor who joined UCR's Department of Physics and Astronomy in 2004. "They display properties that resemble both particles and waves."
Lau observed that when the electrons are reflected from one of the boundaries of graphene, the original and reflected components of the electron can interfere with each other, the way outgoing ripples in a pond might interfere with ripples reflected back from the banks.
Her lab detected the "electronic interference" by measuring graphene's electrical conductivity at extremely low (0.26 Kelvin) temperatures. She explained that at such low temperatures the quantum properties of electrons can be studied more easily.
"We found that the electrons in graphene can display wave-like properties, which could lead to interesting applications such as ballistic transistors, which is a new type of transistor, as well as resonant cavities for electrons," Lau said. She explained that a resonant cavity is a chamber, like a kitchen microwave, in which waves can bounce back and forth.
In their experiments, Lau and her colleagues first peeled off a single sheet of graphene from graphite, a layered structure consisting of rings of six carbon atoms arranged in stacked horizontal sheets. Next, the researchers attached nanoscale electrodes to the graphene sheet, which they then refrigerated in a cooling device. Finally, they measured the electrical conductivity of the graphene sheet.
Graphene, first isolated experimentally less than three years ago, is a two-dimensional honeycomb lattice of carbon atoms, and, structurally, is related to carbon nanotubes (tiny hollow tubes formed by rolling up sheets of graphene) and buckyballs (hollow carbon molecules that form a closed cage).
Scientifically, it has become a new model system for condensed-matter physics, the branch of physics that deals with the physical properties of solid materials. Graphene enables table-top experimental tests of a number of phenomena in physics involving quantum mechanics and relativity.
Bearing excellent material properties, such as high current-carrying capacity and thermal conductivity, graphene ideally is suited for creating components for semiconductor circuits and computers. Its planar geometry allows the fabrication of electronic devices and the tailoring of a variety of electrical properties. Because it is only one-atom thick, it can potentially be used to make ultra-small devices and further miniaturize electronics.
Lau, whose research focuses on nanowires, carbon nanotubes, graphene and other organic molecules, was joined in the research by UCR's Feng Miao, Sithara Wijeratne, Wenzhong Bao, Yong Zhang and Ulas C. Coskun. The research was performed at UCR. Currently, Zhang is at Southwest University, China; Coskun is at Duke University, N.C.
UCR startup funds and the UCR Center for Nanoscale Science and Engineering supported the research.
####
About UC Riverside
The University of California, Riverside is a doctoral research university, a living laboratory for groundbreaking exploration of issues critical to Inland Southern California, the state and communities around the world. Reflecting California's diverse culture, UCR's enrollment of about 17,000 is projected to grow to 21,000 students by 2010. The campus is planning a medical school and already has reached the heart of the Coachella Valley by way of the UCR Palm Desert Graduate Center. With an annual statewide economic impact of nearly $1 billion, UCR is actively shaping the region's future. To learn more, visit http://www.ucr.edu or call (951) UCR-NEWS.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
News Media Contact:
Name: Iqbal Pittalwala
Phone: 951.827.6050
Email:
Jeanie Lau
research team leader
Feng Miao
first author
Copyright © UC Riverside
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Dept. of Physics and Astronomy
Dept. of Physics and Astronomy
![]() Center for Nanoscale Science and Engineering
Center for Nanoscale Science and Engineering
| Related News Press |
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








