Home > Press > Pairing Nanoparticles with Proteins
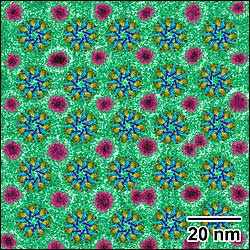 |
| A cryo-electron micrograph showing a single layer of evenly spaced enzyme structures (colorful "wheels") interspersed with gold nanoparticles (magenta). Constructing such regular arrays of biomolecules might help develop high efficiency electrodes for biofuels or improve the resolution of cryo-electron microscopy in structural biology. |
Abstract:
New ways to tag, engineer molecules for energy conversion, drug delivery, and medical imaging
Pairing Nanoparticles with Proteins
UPTON, NY | Posted on June 27th, 2007In groundbreaking research, scientists have demonstrated the ability to strategically attach gold nanoparticles -- particles on the order of billionths of a meter -- to proteins so as to form sheets of protein-gold arrays. The nanoparticles and methods to create nanoparticle-protein complexes can be used to help decipher protein structures, to identify functional parts of proteins, and to "glue" together new protein complexes. Applications envisioned by the researchers include catalysts for converting biomass to energy and precision "vehicles" for targeted drug delivery.
The research, which was conducted at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory, will be published in the July 2, 2007 issue of the journal Angewandte Chemie.
"Our study demonstrates that nanoparticles are appealing templates for assembling functional biomolecules with extensive potential impact across the fields of energy conversion, structural biology, drug delivery, and medical imaging," said lead author Minghui Hu, a postdoctoral student working with James Hainfeld, Raymond Brinas, Luping Qian, and Elena Lymar in the Biology Department at Brookhaven Lab.
In the field of energy conversion, scientists have been searching for efficient ways to convert organic fuels such as ethanol into electricity using catalytic electrodes. But making single layers of densely packed enzymes, the functional part of such catalytic electrodes, has been a challenge. This new research shows that precisely engineered gold nanoparticles can be used to "glue" enzymes together to form oriented and ordered single layers, and that these monolayers are mechanically stable enough to be transferred onto a solid surface such as an electrode.
For this research, the scientists attached gold nanoparticles to an enzyme complex that helps drug-resistant tuberculosis bacteria survive, which has been studied by Brookhaven Lab biologist Huilin Li. The researchers suggest that gold nanoparticles might also be tailored to inactivate this enzyme complex, thereby thwarting drug-resistant TB -- a research avenue they may explore in future studies.
In another part of the study, the researchers used proteins found on the surface of adenovirus, a virus that causes the common cold. Previous studies by Broookhaven's Paul Freimuth have characterized how this virus binds to the human cells it infects, and have suggested that modified forms of adenovirus could be used as vehicles to deliver drugs to specific target cells, such as those that make up tumors.
One key to this approach would be to enhance strong binding to the target cells. Toward that end, Hu and Hainfeld's group attached multiple viral proteins to the gold nanoparticles. Such constructs should have increased binding affinity for target cells and their larger size should extend blood residence time for improved drug delivery.
In another application, this new research showed that gold nanoparticles can enhance scientists' ability to decipher the structures and functionally important regions of protein molecules - the workhorses that carry out every function of living cells and whose dysfunction often leads to disease. With added nanoparticles, the "signal-to-noise ratio" and resolution of an imaging technique known as cryo-electron microscopy were significantly increased. This method might enable analysis of small biological macromolecules and complexes that are currently intractable to analyze by cryo-electron microscopy or x-ray crystallography.
Throughout this work, the biggest challenge was to synthesize size-controllable nanoparticles coated with organic molecules designed to react with specific protein sites. Hu explains the steps: "First, we design the specific interactions between gold nanoparticles and the proteins by coating the gold nanoparticles with functional organic molecules using a biocompatible linker. Then we add a genetically engineered sequence of peptides, called a "tag," to the protein molecule, which acts as the binding site for the gold nanoparticles. Finally, we incubate the nanoparticles with the protein solution to allow the nanoparticles and proteins to bind, transfer the solution onto a transmission electron microscopy grid, and analyze the complexes using state-of-the-art electron microscopes."
####
About Brookhaven National Laboratory
This research was funded by Brookhaven's Laboratory Directed Research and Development program, the Office of Environmental and Biological Research within the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science, and by the Institute of General Medical Sciences within the National Institutes of Health. Collaborators on the research include: Huilin Li, Guiqing Hu, Yanbiao Zhang, and Paul Freimuth, all from the Biology Department at Brookhaven, and Joseph Wall, Martha Simon, Beth Lin, and Frank Kito of the Brookhaven Lab scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM) team.
One of ten national laboratories overseen and primarily funded by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), Brookhaven National Laboratory conducts research in the physical, biomedical, and environmental sciences, as well as in energy technologies and national security. Brookhaven Lab also builds and operates major scientific facilities available to university, industry and government researchers. Brookhaven is operated and managed for DOE's Office of Science by Brookhaven Science Associates, a limited-liability company founded by the Research Foundation of State University of New York on behalf of Stony Brook University, the largest academic user of Laboratory facilities, and Battelle, a nonprofit, applied science and technology organization.
Visit Brookhaven Lab's electronic newsroom for links, news archives, graphics, and more: http://www.bnl.gov/newsroom
--
Media & Communications Office (631) 344-2345 phone
Community, Education, Government (631) 344-8350 phone
& Public Affairs Directorate (631) 344-3368 fax
Brookhaven National Laboratory
Upton NY 11973 http://www.bnl.gov
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Karen McNulty Walsh
(631)344-8350
or
Mona Rowe
(631) 344-5056
Copyright © Brookhaven National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








