Home > Press > Rensselaer Researchers Awarded NSF Grant
Abstract:
Possibilities include much more efficient light emitters and solar cells, extremely sensitive chemical and biological sensors, and super-high-density three-dimensional magnetic memory
Rensselaer Researchers Awarded NSF Grant To Study Nano Springs, Rods, Beams
Troy, NY | September 15, 2005
Researchers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute are exploring the potential of nanomechanical systems by making and testing springs, rods, and beams on the nanoscale. They have been awarded a $1.15 million grant from the National Science Foundation for the research.
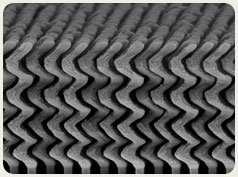
An array of tiny silicon springs, each with a diameter of about 150 nanometers. Copyright © RPI/Toh-Ming Lu |
The past decade has seen an explosion of interest in electronic devices at the molecular level, but less attention has been paid to nanoscale mechanical systems, according to Toh-Ming Lu, the R.P. Baker Distinguished Professor of Physics at Rensselaer and principal investigator for the project. “Nanomechanical devices may have as important an impact as nanoelectronics, but a number of challenges need to be overcome before these systems can be practically realized,” he says. “This represents a multi-billion-dollar high-technology industry that will save energy and improve the quality of lives.”
Lu envisions a wide range of applications for these devices, including much more efficient light emitters and solar cells, extremely sensitive chemical and biological sensors, and super-high-density three-dimensional magnetic memory.
To achieve these advances, researchers need a better understanding of not only the growth and control of nanoscale structures, but also the way they respond to external forces such as heat, electric and magnetic fields, and mechanical stress, according to Lu. He has brought together a team of physicists, materials scientists, and mechanical engineers to address all of these issues.
“This is one more example of the wide array of interdisciplinary research being conducted at Rensselaer,” says Omkaram “Om” Nalamasu, vice president for research at Rensselaer. “Collaborative work like this will help our society solve its most pressing problems in fields as diverse as energy security and information technology.”
The $1.15 million, four-year grant is part of a National Science Foundation program to develop Nanoscale Interdisciplinary Research Teams (NIRT) to catalyze synergistic research and education in emerging areas of nanoscale science and technology.
Nanotechnology at Rensselaer:
In September 2001, the National Science Foundation selected Rensselaer as one of the six original sites nationwide for a new Nanoscale Science and Engineering Center (NSEC). As part of the U.S. National Nanotechnology Initiative, the program is housed within the Rensselaer Nanotechnology Center and forms a partnership between Rensselaer, the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, and Los Alamos National Laboratory. The mission of Rensselaer’s Center for Directed Assembly of Nanostructures is to integrate research, education, and technology dissemination, and to serve as a national resource for fundamental knowledge and applications in directed assembly of nanostructures. The five other original NSECs are located at Harvard University, Columbia University, Cornell University, Northwestern University, and Rice University.
About Rensselaer:
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, founded in 1824, is the nation’s oldest technological university. The university offers bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees in engineering, the sciences, information technology, architecture, management, and the humanities and social sciences. Institute programs serve undergraduates, graduate students, and working professionals around the world. Rensselaer faculty are known for pre-eminence in research conducted in a wide range of fields, with particular emphasis in biotechnology, nanotechnology, information technology, and the media arts and technology. The Institute is well known for its success in the transfer of technology from the laboratory to the marketplace so that new discoveries and inventions benefit human life, protect the environment, and strengthen economic development.
For more information, visit www.rpi.edu
Contact:Jason Gorss
Science Writer/Media Relations Specialist
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
110 8th Street/Hedley Building
Troy, NY 12180
phone: 518-276-6098
fax: 518-276-6091
gorssj@rpi.edu
Copyright © Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Investments/IPO's/Splits
![]() Daikin Industries becomes OCSiAl shareholder July 27th, 2021
Daikin Industries becomes OCSiAl shareholder July 27th, 2021
![]() INBRAIN Neuroelectronics raises over €14M to develop smart graphene-based neural implants for personalised therapies in brain disorders March 26th, 2021
INBRAIN Neuroelectronics raises over €14M to develop smart graphene-based neural implants for personalised therapies in brain disorders March 26th, 2021
![]() 180 Degree Capital Corp. Issues Second Open Letter to the Board and Shareholders of Enzo Biochem, Inc. March 26th, 2021
180 Degree Capital Corp. Issues Second Open Letter to the Board and Shareholders of Enzo Biochem, Inc. March 26th, 2021
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








